Research Achievement
2015
2차원 또는 3차원 물질에 존재하는 위상효과는 위상 절연체를 통해서 잘 알려져 있지만, 1차원에서는 단순한 토이모델 이상으로 알려진 바가 없다. 본 연구에서는 실리콘 표면에서 형성된 인듐 나노선이 지금까지 알려진 바 없는 특이한 위상 특성을 가진다는 것을 보이고, 여기서 형성되는 특이한 전자구조를 가지는 솔리톤의 존재를 이론과 실험으로 규명하고, 카이럴 솔리톤 (chiral soliton) 이라 명명하였다. 실리콘 표면에 형성된 인듐 나노와이어는 저온에서 전하밀도파를 형성하며, 4개의 에너지가 동일한 기저상태를 가진다. 4개의 기저 상태에서 전자들의 분포는 조금씩 다른데, 4개의 기저 상태를 순서대로 돌아서 처음의 상태로 돌아올 때, 전자들의 분포는 처음과 동일하지만, 전자들이 왼쪽으로 한 주기 이동하는 효과가 생긴다. 이러한 전하펌핑 개념은 30년전부터 알려지 있었지만, 지금까지는 외부에서 전자기파를 인가하는 경우에만 가능한 것으로 알려져 왔다. 본 연구에서 인듐 나노선에서는 외부 전자기파 없이 4개의 기저상태를 순서대로 돌아감으로써 전하 펌핑이 가능하다는 것을 세계 최초로 밝혔다. 4개의 기저상태를 돌아가는 것은 해당 기저상태 간의 계면인 솔리톤을 순서대로 나노선을 통해 흘리는 것으로 구현 가능하다. 기저상태가 돌아가는 방향에 따라 2종류의 솔리톤이 존재하며, 각각 왼쪽 또는 오른쪽으로 전하펌핑을 한다. 1차원 나노선이 시간에 따라 기저상태가 변해가는 것을 2차원계에 맵핑할 수 있는데, 전하펌핑이 있는 경우는 소위 chiral edge state를 가지는 위상부도체로 맵핑이 된다. 따라서 전하펌핑을 하는 2종류의 솔리톤을 각각 right-chiral과 left-chiral 솔리톤으로 명명하였다. 본 연구가 1차원 위상체 연구의 지평을 넓히는 중요한 계기가 되리라 기대한다.
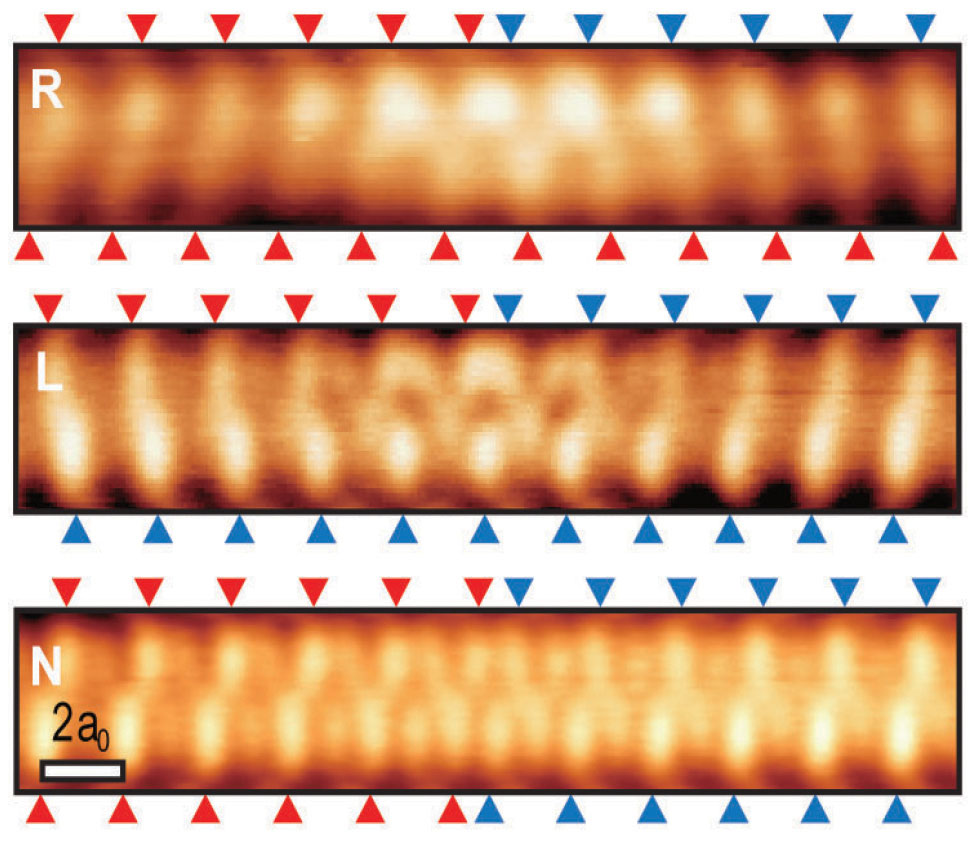
Figure 1. Scanning tunneling microscopy images of three different solitons, right-chiral (R), left-chiral (L), and non-chiral (N) solitons, along in atomic wires.
Chiral edge states are the hallmark of two- and three-dimensional topological materials, but their onedimensional (1D) analog has not yet been found. We report that the 1D topological edge states, solitons, of the charge density wave system of indium atomic wires self-assembled on a silicon surface have chirality. We found that the systems is described by a coupled double Peierls-dimerized atomic chain, where the interchain coupling induced dynamical symmetry breaking. This changes its topological symmetry to Z2 X Z2 to Z4 and endows solitons with a chiral degree of freedom. Chiral solitons can produce quantized charge transport across the chain that is topologically protected and controllable by the soliton’s chirality. Individual right-and left-chiral solitons in indium wires are directly identified by scanning tunneling microscopy. (Science 2015, SHL & HWY)
최근 원자 수준의 이차원 물질은 삼차원 물질과 구별되는 특이 물성으로 인하여 차세대 소자물질로서 각광받고 있다. 특히, 탄소 단원자막, 그래핀은 매우 우수한 전하이동도, 반정수 양자홀 효과와 같은 디랙 입자의 특이 물성을 보여, 지난 10년간 고체물리학 및 재료과학분야에서 집중적인 연구대상이 되었다. 하지만 고유 밴드갭이 존재하지 않기 때문에 준도체적 성질을 띠며 이로 인하여 디바이스로 구성하였을 경우 낮은 on-off ratio값을 갖는다는 한계가 있다. 때문에 최근에는 유한한 고유 밴드갭을 갖는 전이금속 칼코게나이드 혹은 흑린 박막과 같은 반도체 성질을 갖는 이차원 물질들이 주목 받고 있다. 흑린의 한 겹에 해당하는 포스퍼린의 경우 구조적으로 그래핀과 상당히 유사하나, 약 0.3 eV 정도의 고유 밴드갭을 갖고 있다. 이 고유 밴드갭의 크기를 외부 전기장 혹은 압력인가 등의 방법을 통하여 자유자재로 조절할 수 있으면, 전하이동도와 on-off ratio 사이에 적당한 균형을 맞출 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 광전 소자에 폭넓게 활용할 수 있다. 이번 연구에서는 흑린의 표면에 칼륨 원자를 증착하는 방법을 이용하여 고유 밴드갭의 크기를 0~0.6 eV 범위에서 연속적으로 조절하는데 성공하였다. 이는 전계 효과로 2차원 물질의 전자 물성을 반도체로부터 준도체에 이르기까지 선택적으로 제어하는 기술에 해당한다. 뿐만아니라, 고유밴드갭 값이 0에 가까운 반도체- 준도체 전이 임계점에서, 비등방적 디락 전자를 전도 입자로 갖는 독특한 양자상태를 최초로 발견하기도 하였다. 이는 향후 2차원 물질로 이루어진 초소형, 고성능 전자소자 및 광전소자 실현을 위해 유용한“전자물성 제어기술”에 해당한다.
Figure 2. Schematic for few-layer black phosphorus doped with alkali-metal atoms. Purple balls and sticks show the lattice structure of black phosphorus, and the blue balls represent potassium dopants.
Black phosphorus consists of stacked layers of phosphorene, a two-dimensional semiconductor with promising device characteristics. We report the realization of a widely tunable band gap in few-layer black phosphorus doped with potassium using an in situ surface doping technique. Through band structure measurements and calculations, we demonstrate that a vertical electric field from dopants modulates the band gap, owing to the giant Stark effect, and tunes the material from a moderate-gap semiconductor to a band-inverted semimetal. At the critical field of this band inversion, the material becomes a Dirac semimetal with anisotropic dispersion, linear in armchair and quadratic in zigzag directions. The tunable band structure of black phosphorus may allow great flexibility in design and optimization of electronic and optoelectronic devices. (Science 2015, KSK)
위상절연체나 단원자막 반도체와 같은 단순한 전자밴드구조론으로 이해되는 물질을 넘어서, 원자단위 저차원계의 연구는 전자상호작용이 강한 단원자막과 층상 저차원물질의 연구로 빠르게 전개되고 있다. 본 연구단의 연구내용은 계획 단계부터 이러한 연구의 전개를 시야에 넣고 있었으며, 본 연도에는 이러한 연구의 시작으로서, 전자상호작용이 강한 새로운 원자막물질로서의 IrTe2의 원자수준 물성연구에 성공하였다. 본 연구 업적에서는 우선 현재 이 물질계에서 가장 많이 논의되는 저온 stripe charge order상의 chare order를 원자수준에서 관찰하는데 세계 최초로 성공하였다. 또한 이와 별도로 새로운 hexagonal charge order 상이 존재함을 세계 최초로 발견하여 현재 Phys. Rev. Lett.에 투고 중이다. 현재로서는 해당 물질의 원자수준에서의 물성(전하질서 형성과 전자질서와 전자상호작용의 공존 등)을 밝히는 단계에 있고, 이를 토대도 원자수준에서의 물성제어와 헤테로계면 형성을 위한 연구를 위한 발판이 마련되었다는데 연구단 자체적으로 큰 의미가 있다. 이미 본 연구단에서는 이러한 전자상호작용이 강한 층상물질 위에 초전도물질 (Pb) 원자막과 양자박막을 형성하는데 성공하여 차년도의 주요 연구목표로 삼고있다. 즉, 본 연구는 이러한 새로운 원자막계의 헤테로구조 연구로 이어지는 중요한 시발점을 제공한다.
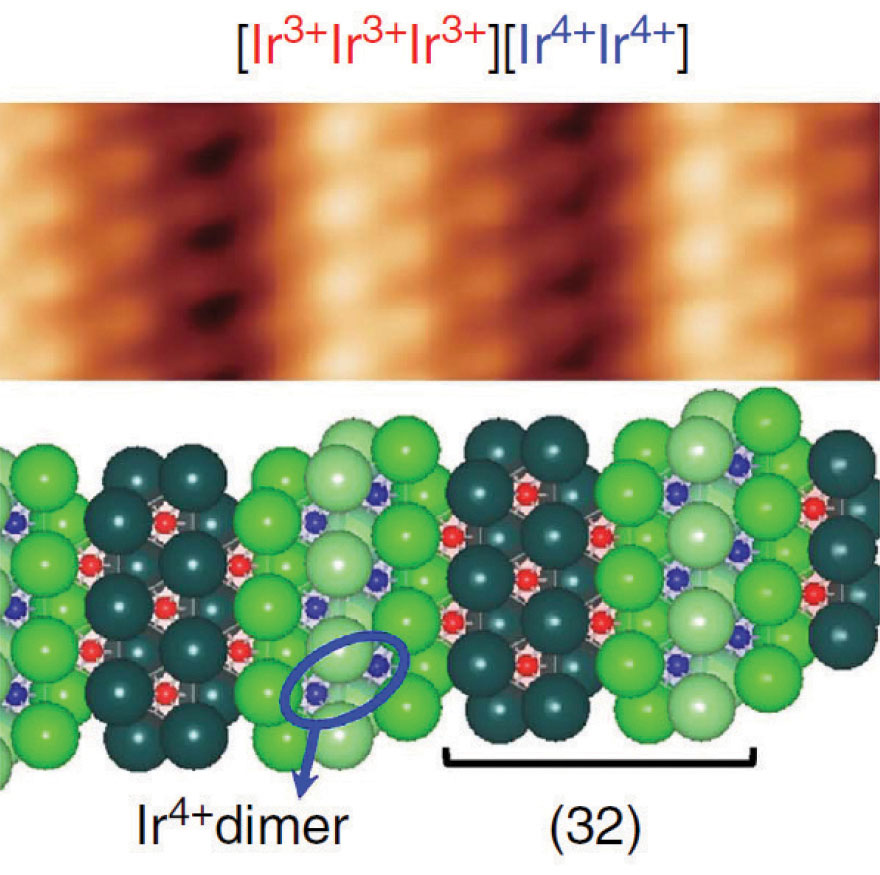
Figure 3. Scanning tunneling microscopy images and schematics of the atomic structures and charge orderings of stripe-ordered IrTe2.
Spin-orbit coupling results in technologically-crucial phenomena underlying magnetic devices like magnetic memories and energy-efficient motors. In heavy element materials, the strength of spin-orbit coupling becomes large to affect the overall electronic nature and induces novel states such as topological insulators and spin-orbit-integrated Mott states. Here we report an unprecedented charge-ordering cascade in IrTe2 without the loss of metallicity, which involves localized spin-orbit Mott states with diamagnetic Ir4+-Ir4+ dimers. The cascade in cooling, uncompensated in heating, consists of first order-type consecutive transitions from a pure Ir3+ phase to Ir3+-Ir4+ chargeordered phases, which originate from Ir 5d to Te 5p charge transfer involving anionic polymeric bond breaking. Considering that the system exhibits superconductivity with suppression of the charge order by doping, analogously to cuprates, these results provide a new electronic paradigm of localized charge-ordered states interacting with itinerant electrons through large spin-orbit coupling. (Nature Comm. 2015, HWY)
본 연구단은 전자상호작용이 강한 이차원물질을 기판으로 하여 새로운 전자물성을 보이는 원자제어 헤테로구조를 생성하는 연구를 장기적인 목표로 추진하고 있다. 이러한 연구를 위해서는 우선 전자상호작용이 강한 이차원 기판물질과 이 기판에 대한 원자수준의 이해 및 제어 기법이 확립되어야 한다. 이에, 우리는 전자상호작용이 강하여 전하밀도파와 Mott 절연체가 공존하는 매우 특이한 이차원물질인 1T-TaS2 기판에 대한 주사터널현미경연구를 진행하고 있다. 특히, 이 물질은 외부자극을 통해 전하밀도파를 조절하여 새로운 초고속 소자에 응용이 가능하며 또한 새로운 형태의 이차원 초전도현상이 거론되어 왔다. 본 연구에서는 이 물질의 전하밀도파를 나노스케일에서 전기적인 펄스로 조절이 가능함을 밝혀 초고속나노소자의 가능성을 개척하였으며, 또한 초전도로 이어지는, 전하밀도파가 붕괴된, 금속상태의 물리적인 기원을 밝혔다. 이 연구는 향후 이차원에서 새로운 초전도 현상에 대한 연구와 특이한 헤테로구조의 형성에 대한 연구로 이어질 것이다.
Figure 4. Schematics of nanoscale manipulation of the CDW-Mott phase of 1T- TaS2 based on scanning tunneling microscope.
Quantum states of strongly correlated electrons are of prime importance to understand exotic properties of condensed matter systems and the controllability over those states promises unique electronic devices such as a Mott memory. As a recent example, an ultrafast switching device was demonstrated using the transition between the correlated Mott insulating state and a hidden-order metallic state of a layered transition metal dichalcogenides 1T-TaS2. However, the origin of the hidden metallic state was not clear and only the macroscopic switching by laser pulse and carrier injection was reported. Here, we demonstrate the nanoscale manipulation of the Mott insulating state of 1T-TaS2. The electron pulse from a scanning tunneling microscope switches the insulating phase locally into a metallic phase which is textured with irregular domain walls in the charge density wave (CDW) order inherent to this Mott state. The metallic state is a novel correlated phase near the Mott criticality with a coherent feature at the Fermi energy, which is induced by the moderate reduction of electron correlation due to the decoherence in CDW. This work paves the avenue to ward novel nanoscale electronic devices based on correlated electrons. (Nature Comm. In press, HWY)
서로 다른 단일원자층 2차원반도체를 수직하게 쌓아 형성한 적층구조에서는 원자층간의 상호작용으로 인하여 다양한 전기적, 광학적, 광기전성 특성을 보인다. 특히, 육각형 격자구조를 가지는 단일원자층 2차원반도체는 육각형 역격자공간의 가장자리에 직접 천이 밴드갭을 가지고 있는데, 이는 수직적 층구조에서의 층간상호 작용이 서로 다른 단일원자층간 회전각도에 의해서 달라질 수 있음을 시사한다. 그러나 그동안 두 원자층간의 결정방향이 정확하게 일치하는 적층구조를 구현할수 있는 물질시스템의 부재로 회전각도에 따라 변화하는 층간 상호작용에 관한 연구는 부재하였다. 본 연구단은 화학 기상증착법을 이용한 합성공정으로 회전각과 결정방향이 정확하게 일치하는 이황화몰리브덴(MoS2)와 이황화텅스텐(WS2) 수직적층구조를 합성하는 공정을 개발하여 적층구조의 흡광발광 특성이 직접천이 양상을 보이는 것을 밝혔다. 더불어 결정 방향이 일치하지 않게 회전각도를 주면 간접천이 양상을 보이는 것을 확인, 천이 양상이 조절되는 것을 확인하였다. 이번 연구 결과로 2차원 원자층반도체적 층구조에서 회전각도가 원자층간의 상호작용에 결정적인 영향을 미친다는 사실을 입증하였으며 결정방향이 일치할 경우 층간 상호작용이 강해진다는 것을 규명하였다.
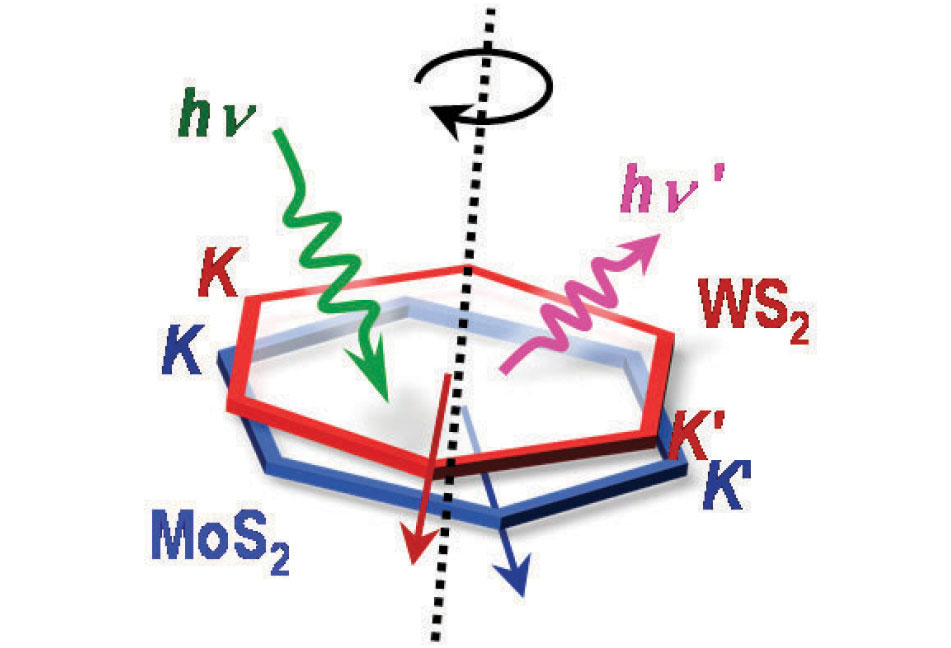
Figure 5. Schematics of this study for light absorption and emission by rotation of monolayer hexagonal semiconductors (MoS2 and WS2) in vertical stacks
Two-dimensional stacks of dissimilar hexagonal monolayers exhibit unusual electronic, photonic and photovoltaic responses that arise from substantial interlayer excitations.
Interband excitation phenomena in individual hexagonal monolayer occur in states at band edges (valleys) in the hexagonal momentum space; therefore, low-energy interlayer excitation in the hexagonal monolayer stacks can be directed by the two-dimensional rotational degree of each monolayer crystal. However, this rotation-dependent excitation is largely unknown, due to lack in control over the relative monolayer rotations, thereby leading to momentum-mismatched interlayer excitations. Here, we report that light absorption and emission in MoS2 /WS2 monolayer stacks can be tunable from indirect- to direct-gap transitions in both spectral and dynamic characteristics, when the constituent monolayer crystals are coherently stacked without inplane rotation misfit. Our study suggests that the interlayer rotational attributes determine tunable interlayer excitation as a new set of basis for investigating optical phenomena in a two-dimensional hexagonal monolayer system. (Nature Comm. 2015, MHJ)
단일층 전이금속 칼코게나이드를 적층함으로써 형성되는 2차원 양자 이종구조의 경우, 강한 층간 상호작용에 의한 전기적/광학적 성질을 나타낸다. 따라서 이러한 이종 접합 적층 구조를 (1) 대면적에서 (2) 단일층간 결정 방향이 제어된 이종접합 물질의 성장은 재료과학적 관점에서 매우 중요하다. 본 연구에서는 대표적인 전이금속 칼코게나이드인 이황화몰리브덴(MoS2)와 이황화텅스텐 (WS2) 단일층을 기상 합성공정을 통해 대면적에서 구현가능하고, 핵 생성 동역학을 제어하여 단일층 간의 이종 수직/수평 접합 구조를 조절할 수 있음을 규명하였다. 특히, 이렇게 형성된 이종 구조의 경우, 두 단일층 간의 결정학적 방향이 일치하는 에피탁시 형태를 보임을 투과전자현미경 분석을 통해 확인하였다. 연속적인 기상 합성공정을 통하여 형성된 층 간의 방향성 차이가 없는 이종 적층 구조의 경우, 일반적으로 개별 단일층을 박리/전사하여 형성한 이종 구조에 비하여 강한 층간 상호작용을 기대할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
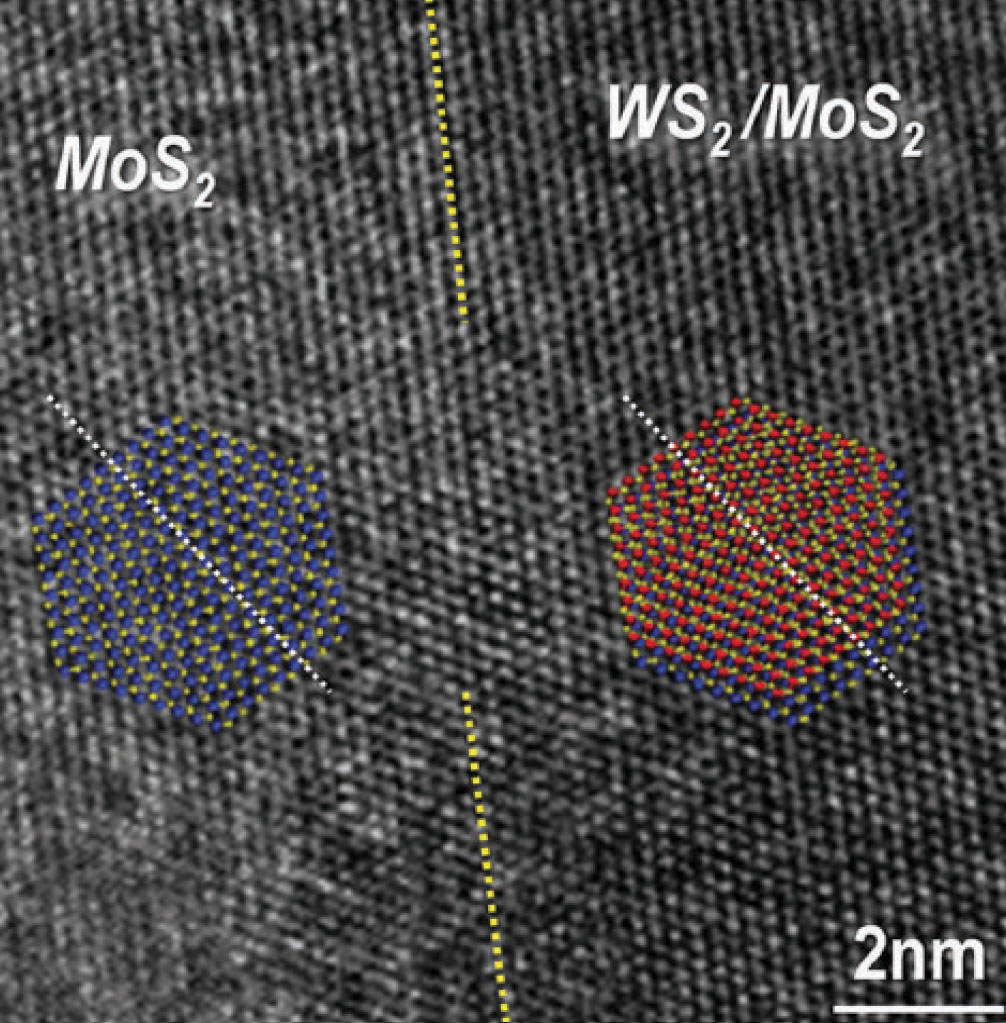
Figure 6. In-plane TEM image at the boundary of the MoS2 and WS2/MoS2 vertical stack region, showing the invariable hexagonal unit cell orientations.
Isolated monolayer (ML) crystals of hexagonal transition-metal dichalcogenides (h-TMDCs) can be manually stacked to form atomic 2D heterostructures, showing the inter-ML coupled electronic and photonic responses. Nevertheless, from the materials science' point of views, there remain two fundamental issues to be resolved. First, controlled large-area growth of the ML heterostructures is not available and second the precise control over the crystallographic rotations of each h-ML in such 2D superstructures is lacking. Here, we show the heteroepitaxial 2D stacking and stitching of MoS2and WS2 MLs, by manipulation of 2D nucleation kinetics during the sequential vapor phase growth.
It enables to create the hexagon-on-hexagon unit cell stacking and the hexagon-by-hexagon stitching without interlayer rotation misfits. The scalable 2D hetero-integrations of ML crystals into such coherent stacking and stitching units may provide an innovative design rule of the 2D h-TMDC heterostructures as the novel electronic and optical semiconductor platforms in large-areas, yet precisely controlled at the ultimate size limt. (Adv. Mater. 2015, MHJ)
반데르발스물질의 경우 층간의 약한 결합 특성으로 인하여 수 원자층 두께를 가지는 2차원 층상 구조를 가진다. 이러한 구조적 특징으로 인해 2차원 물질들은 3차원 벌크물질과는 다른 새로운 저차원 전자 시스템을 제공한다. 전이금속칼코게나이드의 경우, 구성 원소간의 화학결합 배위양상에 따른 다양한 조성비의 화합물을 가지며, 이에 따라 상이한 물성이 기대 되어진다. 일반적으로 알려진 2차원 원자층물질의 경우 (그래핀, 육방정계질화붕소, 전이금속칼코겐화합물) 육방정계 (hexagonal)의 구조를 가지는 반면 사방정계 (orthorhombic) 구조를 가지며 자발적으로 성장하는 2차원 원자층도 존재한다. 다만, 사방정계구조의 2차원 원자층물질은 구조 성장 중의 열역학적 불안정성으로 인하여 상대적으로 알려진 바가 적다. 본 연구단은 기상합성 공정단계에서 공정기체분위기를 조절하는 방법으로 2차원 원자층황화주석화합물을 육방정계구조 (SnS2)와 사방정계구조 (SnS)를 선택적으로 성장할 수 있는 공정개발에 성공하였다. 특히, 육방정계구조의 황화주석의 경우 밴드갭의 크기가 2.77 eV인 N형 반도체이고 사방정계구조의 황화주석은 밴드갭 크기가 1.26 eV인 P형 반도체로 선택적성장을 통한 황화주석 p-n 접합을 제작할 수 있었다. 형성 2차원황화주석 p-n 접합을 이용하여 정류기, 광전지 그리고 인버터소자를 구현하였다.
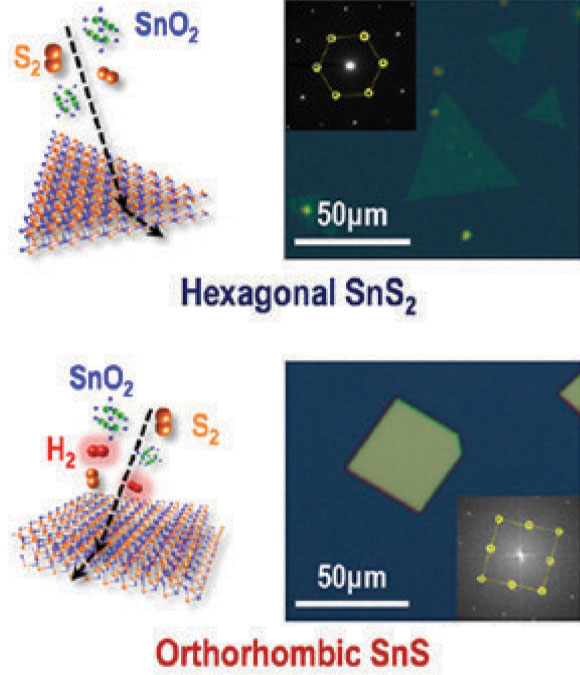
Figure 7. Growth schematics and representative optical microscope images & TEM FFT-diffraction patterns of hexagonal SnS2 in N2 and orthorhombic SnS in N2-H2.
Van der Waals layered materials have large crystal anisotropy and crystallize spontaneously into twodimensional (2D) morphologies. Two-dimensional materials with hexagonal lattices are emerging 2D confined electronic systems at the limit of one to three atom thickness. Often these 2D lattices also form orthorhombic symmetries, but these materials have not been extensively investigated, mainly due to thermodynamic instability during crystal growth. Here, we show controlled polymorphic growth of 2D tinsulfide crystals of either hexagonal SnS2 or orthorhombic SnS. Addition of H2 during the growth reaction enables selective determination of either ntype SnS2 or p-type SnS 2D crystal of dissimilar energy band gap of 2.77 eV (SnS2) or 1.26 eV (SnS) as a final product. Based on this synthetic 2D polymorphism of p-n crystals, we also demonstrate p-n heterojunctions for rectifiers and photovoltaic cells, and complementary inverters. (Nano Lett. 2015, MHJ)
스핀각도분해 광전자분광 장치는 통상적인 각도분해 광전자분광의 전자밴드 구조 측정 기능에 더하여 스핀 분리된 전자밴드 구조를 직접적으로 측정하는 기술에 해당한다. 본 연구단은 포항가속기연구소의 강력한 방사광원과 저에너지 전자회절 방식의 고효율 스핀 검출기를 결함하여 최고 수준의 분해능을 갖는 스핀각도분해 광전자분광 장치 구축을 목표로 한다. 가속기연구소와 체결한 양해각서를 바탕으로 본 연구단은 엔드스테이션 장비를 구축하며, 가속기 측에서는 본 장비가 결합될 빔라인의 업그레이드를 자체적으로 진행 중이다.
연구단은 2015년 9월 스핀디텍터를 포함한 전체 시스템의 설계 및 주문을 완료하였다. 현재 포항가속기 측의 요청에 의해 스핀분해 기능에 우선하여 각도분해 광전자분광 부분을 먼저 구축 완료한 후 유저 지원을 시작하고, 스핀 분해 기능을 순차적으로 구축하는 순서로 계획을 수정하였다. 2016년 2월 현재 스핀 검출기 부분을 제외한 엔드스테이션 부분은 구축 완료 되었으며, 헬륨방전램프를 이용한 성능 테스트도 성공적으로 수행 되었다. 본 장치는 2016년 3월까지 포항가속기 4A1빔라인과 연결하여 유저지원을 시작할 예정이며, 이어 스핀검출기 제작에 착수한다.
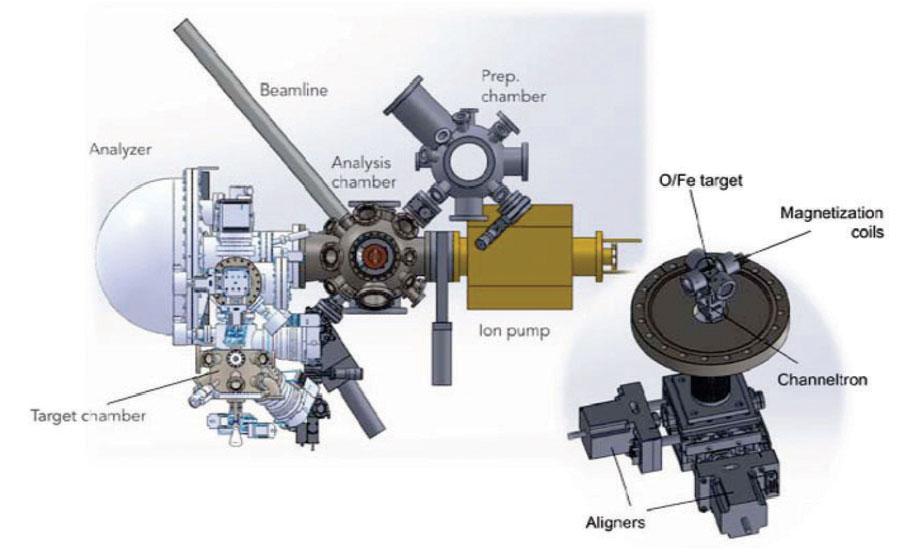
Figure 8. Schematic drawing of SARPES system with VLEED-type spin detectors.
Spin-and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (Spin-ARPES) is capable of probing spin-split electronic band structure of solids. CALDES develops the spin-ARPES system, which will be attached to one of undulator beamlines in Pohang Light Source (PLS). We combine the state-of-the-art ARPES technique with the exchange-scattering-type spin detectors with an efficiency substantially higher than conventional Motttype spin detectors. This system will be the unique spin-ARPES system with the highest performance in the world when finished. The basic design of the Spin-ARPES endstation was finished in 2014 as shown below. One small change in the plan is that, to minimize the loss of user’s beamtime in PLS, we decide to develop the ARPES part first, and then attach the spin detectors later on. Major components, such as electron spectrometer, He-discharge UV lamp, ultrahigh vacuum chamber, and frames, have been delivered, and most of the system are constructed as shown below. The manipulator will be delivered in November, 2015, and then we have all in hand to finish building up the ARPES system. The test operation of ARPES with a He-discharge lamp will be conducted by January 2016, and the whole system will be connected to the PLS beamline in between February 2016 ~ April 2016. We will continue the user support, right after certain period of commissioning beamtime for ARPES, after which developments of spin detectors will be followed. We expect that ARPES combined with PLS will be fully operational before September, 2016. (KSK)
기초과학원연구원(Institute for Basic Science, IBS)의 원자제어 저차원 전자계연구단 (Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems, CALDES)의 자기힘현미경연구실은 액체헬륨-3냉동기와 삼차원으로 구성된 초전도 자석을 이용하여, 최저온도 300 mK 그리고 삼 차원 자기장을 인가할 수 있는 극저온 벡터 자기장 MFM을 세계최초로 2014년에 구축하였고, 특이한 현상을 나타내는 스커미온 자성체와 철계/무거운 페르미온 초전도체에 응용하고 있다. 최근에 강자성 초전도 체인 ErNi2B2C에서 초전도와 자성도메인이 공존하는 것을 직접적으로 관찰하여 Phys. Rev. B (2015)에 출판되었다. 현재 벡터자장을 사용하여 초전도물성의 비등방성에 관해 심도 있는 연구가 진행되고 있다.
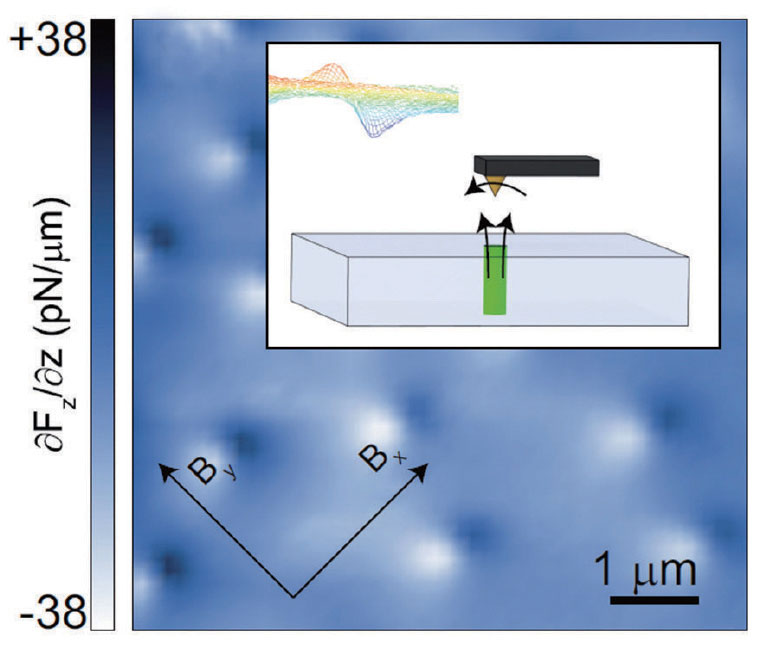
Figure 9. Image of magnetic vortices in a superconducting Nb film obtained by our 3He magnetic force microscope
Magnetic force microscope (MFM) laboratory has constructed a very low temperature, the lowest in the world, MFM, operating within a vector magnet with the base temperature of 300 mK and magnetic field range of 2-2-9 T in the x-y-z direction. The microscope employed a low-noise fiber optic interferometer system including two home-built piezo walkers for the fine alignment between fiber and cantilever. The noise level of the system is close to its thermodynamic limit with a minimal detectable force gradient of 3 10-7 N/m. The performance of the apparatus was demonstrated by the creation and imaging of Abrikosov vortices within a superconducting Nb film using a vector field. For example, an in-plane field allows creating a vortex-antivortex pair which is confined through a single flux tube, and thus showing a linear potential in distance. This work will be submitted together with a theoretical result.
In addition, we demonstrated magnetic imaging capabilities at very low temperature by imaging simultaneously superconducting vortices and magnetic stripes at T= 500 mK in the ferromagnetic superconductor ErNi2B2C which has a ferromagnetic transition below T= 2.3K. The direct visualization of coexistence between superconductivity and magnetism was carried out in ErNi2B2C, for the first time, which has been published in Phys. Rev. B(2015). Our LT-MFM with vector magnet capabilities opens the door to directly observe and study magnetic and superconducting phenomena emerging at very low temperatures, such as magnetically mediated superconductivity in heavy fermion systems, nonlinear Meissner effect in superconductors, and superconductivity with an anisotropic pairing symmetry. It furthermore allows us to study the magnetic behavior of domain formation and evolution within a 3-dimensional freely rotatable magnetic field. (JHK)
극저온 고자기장 주사 터널 현미경에 사용될 냉동기는, 현재 제작 완료에 근접해있다. 강력한 냉동 파워 (100mK에서 800 micro Watt)와 벡터형 초전도 자석(9+2+2 Tesla)을 갖추게 되어, 기존 존재하는 다른 극저온 고자기장 주사터널 현미경들보다 더 낮은 실험온도를 구현할 수 있을 것이다. 냉동기 테스트가 끝나면 2016년 1월경에는 배송작업이 시작될 것이다. 본 연구단의 극저온 고자기장 주사 터널 현미경은 하방 장착 스타일이어서, 탐침과 샘플이 냉동기 아래를 통해서 초전도 자석 중심 센터로 들어가는 방식이다[Fig.10 참조]. 탐침과 샘플의 교환이 용이하게 설계하였으며, 2016년 안에 주사터널 현미경 헤드가 만들어서 테스트 작업에 들어갈 것이다. 진동방지 시설은 포항공과대학교의 지원으로 2015년에 완공되었다. 2016년에는 진동방지 테이블 위에 극저온 고자기장 주사터널 현미경이 설치될 예정이다.
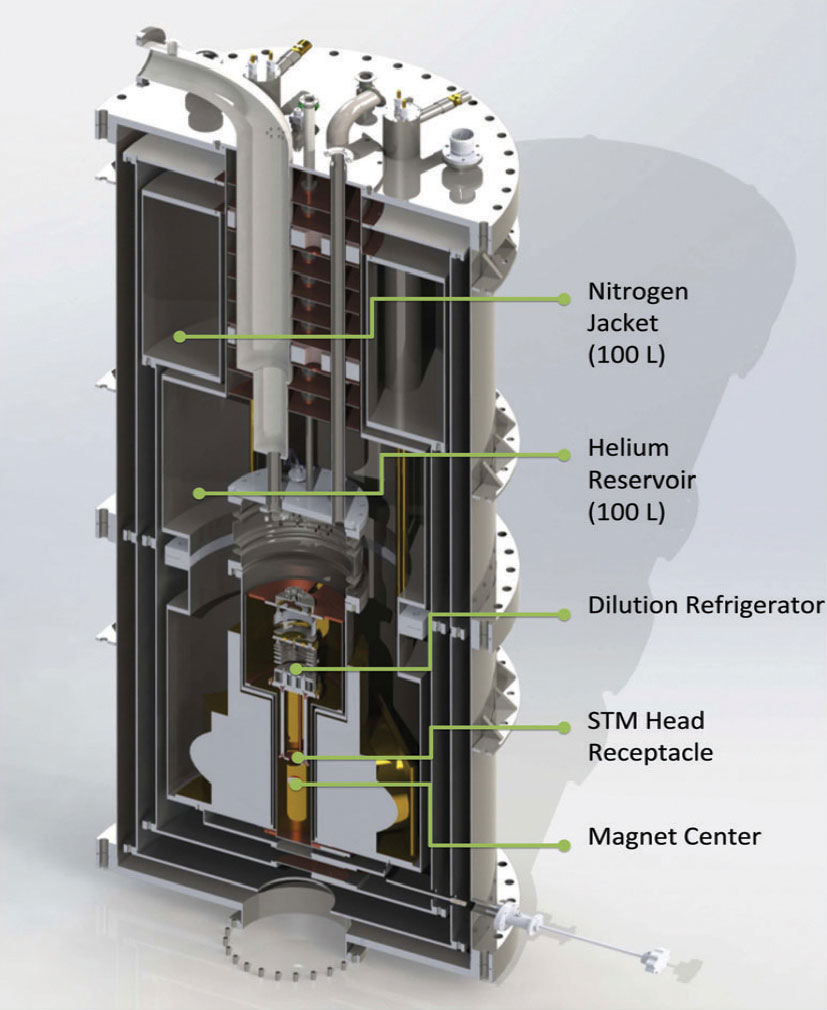
Figure 10. Schematic of dilution refrigerator with superconducting magnets
Our cryostat for ultralow temperature high magnetic field STM is at the final stage of construction. With a unique combination of the strong cooling power (800 micro Watt at 100 mK) and a vector superconducting magnet (9+2+2 Tesla), we expect to carry out high field experiments at lower temperature than any other ultralow temperature high magnetic field STM’s in the world (Figure below). The cryostat insert is being leaktested at low temperatures. After the test, STM wiring will be finished and a superconducting magnet will be combined with the cryostat insert. The whole assembly of cryostat will be shipped by the mid-January of 2016.
The design of our ultralow temperature high magnetic field STM is so-called “bottom loading”, which means that STM tips and samples are transferred through the bottom of the cryostat to the center of the superconducting magnet (see Figure). The STM has been designed in such a way that operators can exchange tips and samples easily, and can deposit various materials on the sample surface easily at room temperature or 4K. The prototype STM scanner has been constructed and tested in 2015.
Vibration isolation facilities for ultralow temperature precision measurements have been constructed with the support from POSTECH in 2015. In 2016, ultralow temperature high magnetic field scanning tunneling microscope will be installed on the vibration isolation table. (UDH)
나노융합원과 포항공과대학교의 지원으로 무진동 건물이 완공되었다. 건물이 완공된 직후에 진동 방지 시설이 설치되어, 극저온 고자기장 주사터널 현미경, 자기력 현미경, 그리고 고자기장 전자수송 실험이 가능케 한다. 2016년 1월 현재, 한 개의 진동 방지 시설은 사용 중이며, 나머지 두 개는 2016년 안에 장비가 설치될 것이다. 현재, 압축공기, 질소 가스, 냉각수 등의 각종 유틸리티 시설이 2015년에 설치되었다. 또한 헬륨 회수 및 헬륨 액화 설비가 완성되어 일주일에 1000 리터의 액체 헬륨이 공급되어 플래그쉽 장비에 사용될 것이다.
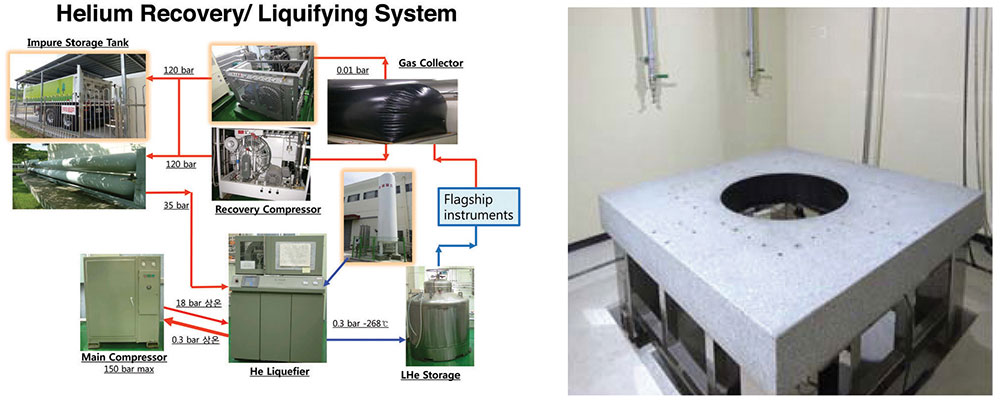
Figure 11. Schematic of helium recovery / liquefying system(left) and vibration isolation table with active damping(right)
The building accommodating large scale vibration isolation facilities was built with the support from the National Institute for Nanomaterials Technology (NINT) as well as POSTECH in the middle of 2015. Just after the building was completed, three vibration isolation facilities were installed for an ultralow temperature high magnetic field scanning tunneling microscope, a magnetic force microscope, and a high magnetic transport instrument, respectively. Two of them are specially designed with high inertia mass (up to 40 tons) of floating base for very low vibration. A vibration isolation facility is being used since this summer and the other two are ready to install new equipment in the early next year. Currently, we installed several lab utilities in order to provide compressed air, dry nitrogen gas, cooling water, etc. We have successfully established a helium recovery and liquefying system, which will supply liquid helium (1000 liters/week) sufficient for running all the flagship instruments mentioned above. (UDH)
 Center for Artificial Low
Center for Artificial Low