Research Achievement
2022
본 연구에서는 기존에 장기간에 걸쳐 진행하고 있는 연구단의 핵심연구주제인 일차원 전자계의 솔리톤연구에 있어서 중요한 새로운 발견을 보고하였다. 기존에 연구된 솔리톤은 주로 Z2 대칭성을 가지거나 본 연구단이 2015년 Science에 발표한 바와 같이 Z4 대칭성을 가지는데, 이들은 모두 정수의 전하를 가지고 있다. 하지만 이미 1980년 초부터 이와는 상이한 대칭성에 기반하여 분수정수를 가지는 솔리톤이 예측되었으나 실험적으로 관측된 바 없었다. 본 연구에서는 실리콘 표면에 금을 흡착하여 만들어지는 실리콘 원자선에서 Z3 대칭성을 가지고 분수전하를 띄게 되는 솔리톤을 세계최초로 관측하였고 이를 이론적으로 해석하여 그 위상 학적 성질을 확인하였다.
특히 기판의 온도를 변화시키면서 실시간 측정을 시도하여, 개별 솔리톤의 움직임을 실시간 관측하는 것에 성공하였다. 더욱 더 나아가, 주 사터널현미경으로 국소적인 전류/전압 펄스를 인가하여, 개별 솔리톤을 생성하는 것에 성공하였다. 이러한 일련의 성과는 솔리톤을 제어하는 기본기술을 확보하는 것으로서 향후의 솔리톤의 응용에 중요한 첫 번째 벽을 넘어선 것이라 할 수 있다.
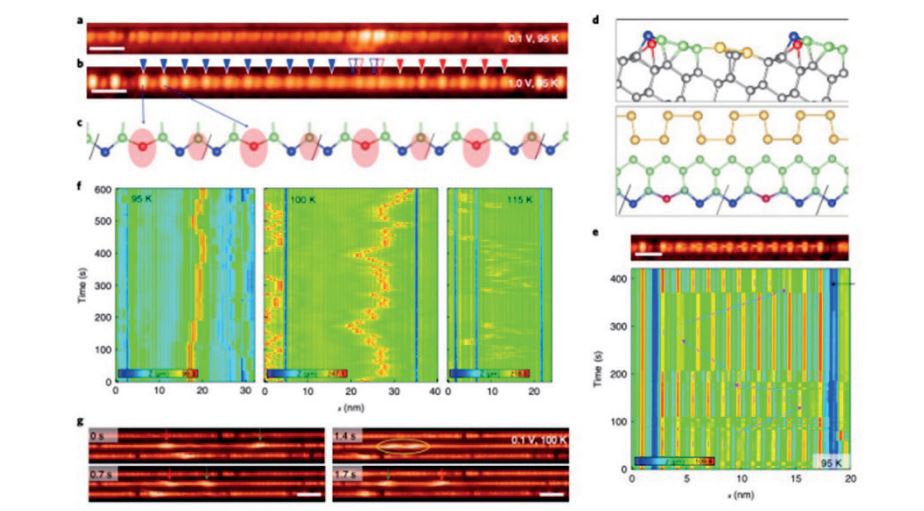
FigureMobile phase defect on Si chain of a Si(553)-Au surface. a, b STM images of phase-shift defect. c, d Atomic structure of a Si step-edge chain. e, f Real time measurement of the STM profiles. g Snapshot STM images of the mobile phase defects.
In this work, we report an important breakthrough in the research of solitons in electronic systems. Using a Z3 symmetric charge density wave system on silicon atomic chains, we discovered a fractionally charge solitons, which was predicted in early 1980’s and have been looked for in last three decades. We could also track the kinetic motion of individual solitons for the first time in the history of electronic solitons. Moreover, we have succeeded in creating individual solitons by electronic pulse from the scanning tunneling microscopy tip. This will be an essential milestone for the further application of solitons in informatics.
빛과 물질의 상호작용을 통해 새로운 양자 상태를 설계하는 것은 물리학 분야 전 반에 새로운 패러다임이 되어 가고 있다. 예를 들어 물질에 빛 등을 통해 시간에 대해 주기적인 외부 자극을 주면 물질의 본래 양자상태가 에너지 방향으로 복제되는 플로케 상태가 구현된다. 이를 통해 자연계에 존재하지 않는 양자상태를 인공적으 로 만들 수 있으며, 이를 활용한 양자정보 분야로의 응용가능성도 넓게 열려 있다. 하지만 지금까지는 측정 방법 및 발열의 한계로, 플로케 상태를 250 펨토초(1 펨 토초는 천조분의 일 초)라는 아주 짧은 시간 동안만 구현할 수 있었다. 이렇게 짧은 지속 시간 때문에 양자역학적 비평형 상태에 대한 정량적 분석이 불가능했으며 다른 플랫폼으로의 확장이 힘들었다. 본 연구진은 마이크로파를 통해 오랫동안 지속되는 플로케 상태를 최초로 구현하고, 이론적 정량분석에 성공했다. 기존의 실험들은 높은 주파수를 가지는 광학 레이저를 사용하였기 때문에 그만큼 강한 빛이 필요했고 열도 많이 발생하여 지속가능한 플로켓 상태를 구현할 수 없었으나, 본 연구진은 이 극복하기 위해 낮은 주파수의 마이크로파를 빛으로 사용하였고, 그 결과 1조배 작은 빛의 세기로도 플로케 상태를 구현할 수 있었고, 열 발생 역시 현저히 줄어 25시간 이상 지속 구현할 수 있었다.
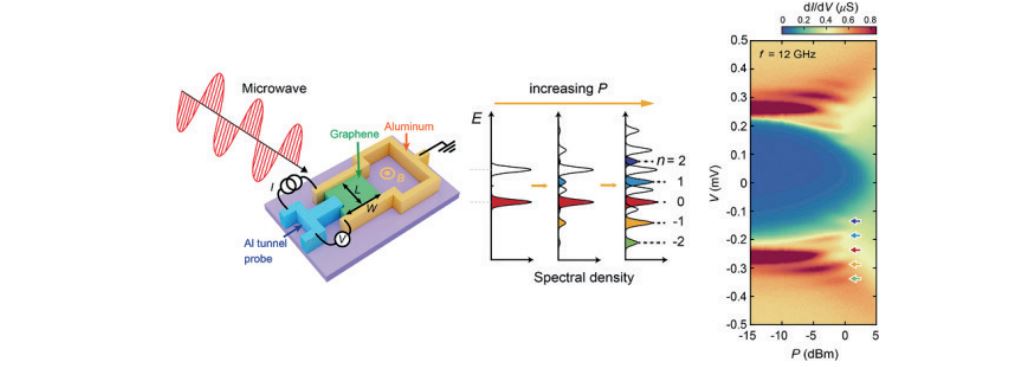
Figure (Left) Schematics of devices realizing Floquet-Andreev Bound states. (Middle) The schematic evolution of the spectral intensities of the Floquet state in terms of irradiated microwave powers. (Right) Experimentally measured spectral intensity of the Floquet states. One can observe that the larger the microwave power is, the more replicas of Floquet states are observed.
Engineering quantum states through light-matter interaction has created a new paradigm in condensed m atter physics. A representative example is the Floquet-Bloch state, which is generated by time-periodically driving the Bloch wavefunctions in crystals. Previous attempts to realise such states in condensed matter systems have been limited by the transient nature of the Floquet states produced by optical pulses, which masks the universal properties of non-equilibrium physics. Here, we report the generation of steady Floquet-Andreev (F-A) states in graphene Josephson junctions by continuous microwave application and direct measurement of their spectra by superconducting tunnelling spectroscopy.
We presen quantitative analysis of the spectral characteristics of the F-A states while varying the phase difference of superconductors, temperature, microwave frequency and power. The oscillations of the F-A state spectrum with phase difference agreed with our theoretical calculations. Moreover, we confirmed the steady nature of the F-A states by establishing a sum rule of tunnelling conductance, and analysed the spectral density of Floquet states depending on Floquet interaction strength. This study provides a basis for understanding and engineering non-equilibrium quantum states in nano-devices.
Nature Materials 21, 1144-1149 (2022)
반데르발스 물질기반 스핀 접합 소자는 높은 결정성과 원자수준에서 깨끗하고 평평한 계면을 형성할 수 있어 스핀트로닉스 소자 응용성이 기대되어 최근 전세계적으로 활발히 연구되고 있다. 다양한 반데르발스 물질을 이용한 스핀 접합 소 자 연구를 통해 다양한 스핀트로닉스 기능성이 확인되었으나 기존 박막기반 스핀 트로닉스의 기능성을 월등히 개선한 결과는 제한적으로 보고되었다. 본 연구에서는 반데르발스 강자성체인 Fe3GeTe2와 반데르발스 부도체인 WS2 또는 hBN 를 이용한 접합 소자를 구성하고 기존 박막소자 대비 획기적으로 넓은 전압 인가 영역에 대해서 스핀 터널자기저항을 조사하였다. 접합에 인가되는 전압을 넓은 영 역으로 조절하여, 강자성체의 스핀 의존 상태 밀도의 급격한 변화를 유도하고 이를 통해 유효한 스핀 분극의 크기와 부호를 인가 전압을 통해 효과적으로 변조하였다. 이는 기존 금속박막 또는 반데르발스/금속 박막 기반의 소자에 비해 반데르 발스 기반 소자가 월등하게 높은 터널자기저항 변화폭을 가진다는 점을 의미할 뿐 만 아니라 인가전압에 따른 스핀 분극 조절이라는 새로운 개념을 제안한 성과이다. 이러한 결과는기존 박막기반 스핀 소자에서 불가능한 기능성을 확인한 드문 사례로, 향후 반데르발스 기반 스핀 정보 소자로의 활용 가능성을 높이는 데 기여 할 것으로 기대된다.
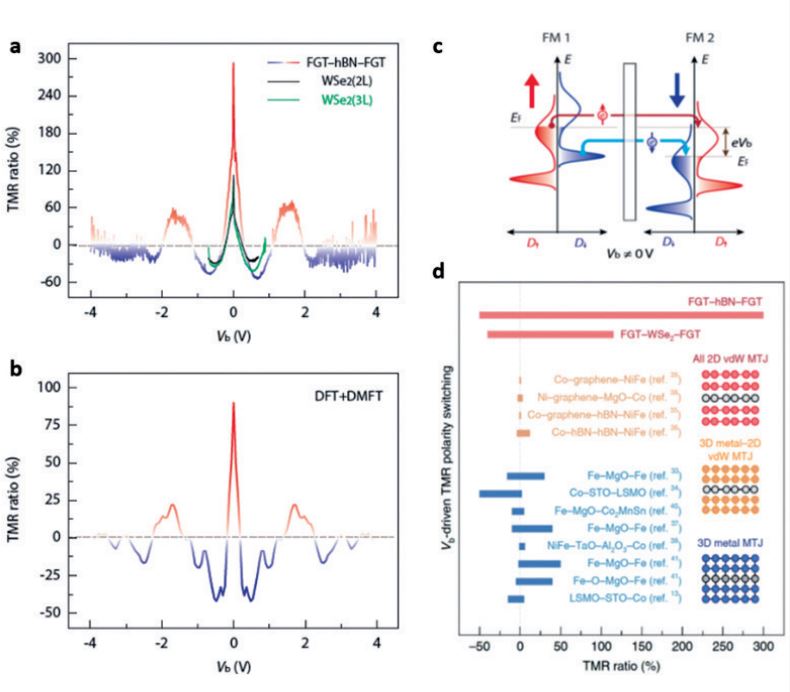
Figure (a) Sign changes of tunneling magnetoresistance as a function of applied bias voltages (b) Calculated spin-dependent density of states (c) Spin tunneling conduction at high applied bias. (d) Comparison of tunneling magnetoresistance with bias voltages for previously-studied magnetic tunnel junctions.
Spin junction devices based on van der Waals materials have been actively researched worldwide due to their high crystallinity and the ability to form clean and flat interfaces at the atomic level. These characteristics are expected to lead to novel applications in spintronics devices. Various spintronics functionalities have been confirmed through the studies of spin junction devices using different van der Waals materials. However, limited results have been reported that significantly improve functionality over those of conventional thin film-based spintronics. In this study, we constructed a junction device using Fe3GeTe2, a van der Waals ferromagnet, and WS2 or hBN, a van der Waals insulator. We investigated the tunnel magnetoresistance over a dramatically wider voltage application region than conventional thin-film devices. By controlling the voltage applied to the junction over a wide area, we induced a rapid change in the spin-dependent density of states, which effectively modulated the magnitude and sign of the spin polarization through the applied voltage. These results not only indicate that van der Waals-based devices have a significantly higher tunnel magnetoresistance variation than conventional metal thin film devices but also propose a new concept of voltage-dependent spin polarization control, which can be utilized in all van der Waals-based spin information devices in the future.
자성 물질의 물리적 특성은 종종 미시적 스핀 및 전자 구조뿐만 아니라 자기구역 형성이나 화학적 또는 전자적 상 분리에서 나타나는 중시적 길이 스케일의 구조에도 의존한다. 그러나 이러한 중시적 구조에 대한 실험적 관찰은 현재 제한적이며, 특히 순자화가 0인 반강자성체의 경우는 관측하기 더욱 까다롭다. 본 논문에서는 온마당 현미경과 공명 자기 엑스선 회절을 결합하여 ≈0.1 mm2이상의 면적을 ≈150 nm공간 분해능으로 스핀-궤도 모트 부도체 Sr2 IrO4의 반강자성 자기구역을 시각화하는데 성공하였다. 전례 없는 넓은 시야와 높은 공간 해상도로 평균 반강자성 자기구역 벽 너비 545nm를 측정하였으며, 이와 비슷한 길이 척도에서 두 반강자성 자기구역의 얽힘이 나타남을 보였다.
이 중시적 구조는 시료 표면의 상당한 부분을 차지하므로 미시적 자기 구조에서 예상하지 못한 거시적 반응을 초래할 수 있다. 특히, 본 연구에서 제시한 대칭성 분석은 미시적인 반강자성 질서에 의해 보존되는 반전 대칭성이 중시적 길이 척도에서 정의하기 힘들어진 다는 것 을 보여준다. 이 결과는 반강자성체의 물리적 특성을 보다 깊게 이해하기 위한 이 새로운 기술의 중요성을 보여준다.
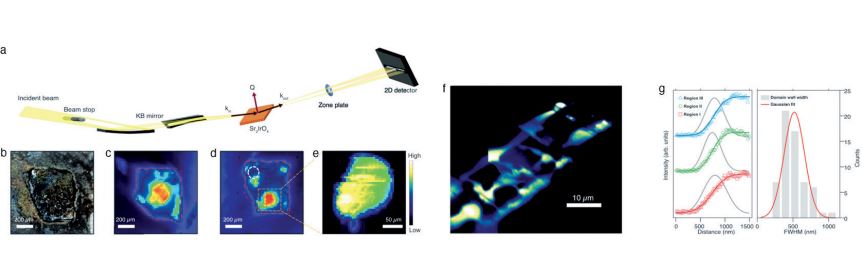
Figure Schematic of our setup. (b) Optical image of the sample. (c,d) False color images for two antiferromagnetic domains obtained by conventional method. (e) Image taken with our new method for the region inside the dotted square box. (f) High-resolution image of nano-scale domains. (g) Analysis of domain wall widths.
The physical properties of magnetic materials frequently depend not only on the microscopic spin and electronic structures, but also on the structures of mesoscopic length scales that emerge, for instance, from domain formations, or chemical and/or electronic phase separations. However, experimental access to such mesoscopic structures is currently limited, especially for anti-ferromagnets with net zero magnetization. Here, full-field microscopy and resonant magnetic X-ray diffraction are combined to visualize antiferromagnetic (AF) domains of the spin-orbit Mott insulator Sr2 IrO4 with area over ≈ 0.1 mm2 and with spatial resolution as high as ≈150 nm. With the unprecedented wide field of views and high spatial resolution, an intertwining of two AF domains on a length comparable to the measured average AF domain wall width of 545 nm is revealed.
This mesoscopic structure comprises a substantial portion of the sample surface, and thus can result in a macroscopic response unexpected from its microscopic magnetic structure. In particular, the symmetry analysis presented in this work shows that the inversion symmetry, which is preserved by the microscopic AF order, becomes ill-defined at the mesoscopic length scale. This result underscores the importance of this novel technique for a thorough understanding of the physical properties of antiferromagnets.
인공적인 2차원 격자시스템은 2차원 체계의 풍부한 물리 현상을 구현 가능케 하며 동시에 새로운 양자 소자 응용을 기대할 수 있다. 특히 강한 상호작용이 내 제된 물질을 통한 위상학적 격자구조의 구현은 초전도체, 모트절연체 등 보다 흥미로운 양자상태의 구현을 이룰 수 있다. 본 연구에서는 2차원 모트절연체인 1T-TaS2의 표면에 금속 흡착에 의한 인공 격자를 구현하는 방법을 제안하고자 하였다. 알칼리, 알칼리토금속, 그룹 13족 금속 원자들이 육방격자 및 카고메격 자 대칭을 갖는 √3×√3와 2×2 초격자구조에 흡착되어, 각각 디락 및 카고메 밴드의 형성을 보였다. 이는 기존 metallic 밴드로 구성된 격자대신 flat 밴드로 형성된 위상학적 전자구조에 해당되며 강한 전자 상호작용은 Kame-MeleHubbard/Kagome-Hubbard 모델의 실험적 구현을 기대할 수 있다. 또한, Mg 흡착 덮임률의 조절을 통해 모트-디락 및 모트-카고메 밴드의 2/3 또는 3/4 밴 드 채움을 유도할 수 있었으며 이는 비페르미 액체 특성을 띄는 초전도상태의 구 현을 가능케 한다. 이러한 인위적인 2차원 강상관계 격자 조절방법은 실험적으로 쉽게 구현될 수 있으며 다른 2차원 flat 밴드 기반 초격자 물질로의 적용이 가능 하다. 향후 스핀-궤도 상호작용 및 자성 특성 변화를 기대할 수 있는 흡착 원자의 조절을 통해 양자 홀 효과 및 unconventional superconductivity 현상에 대한 연구로 발전시킬 계획이다.
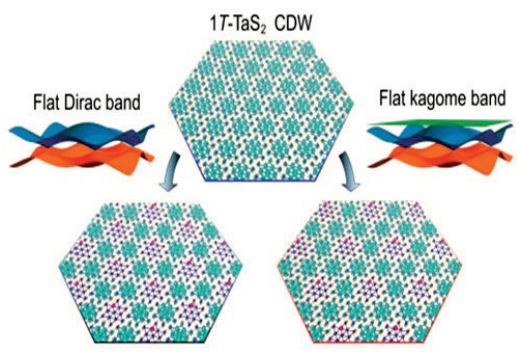
Figure Manipulation of lattice and flat band electronic structure via atomic adsorption on 1T-TaS2CDW.
Artificial two-dimensional (2D) lattice systems enable the realization of rich physical phenomena in 2D systems and offer potential for new applications in quantum device technology. In particular, the implementation of topological lattice structures through flat band materials with strong correlations can lead to the realization of intriguing quantum states. In this study, we propose an approach to realize an artificial lattice by metal adsorption on a 2D Mott insulator 1T-TaS2 . Alkali, alkaline-earth, and group 13 metal atoms are deposited in √3×√3 and 2×2 superlattice structures with hexagonal and Kagome lattice symmetries, respectively, resulting in the formation of Dirac and Kagome bands. These bands correspond to a topological electronic structure composed of flat bands instead of conventional metallic bands, and the strong electronic correlation can potentially lead to the experimental realization of the Kame-Mele-Hubbard/Kagome-Hubbard model. Furthermore, by controlling the coverage of Mg adsorption, we can induce a filling of 2/3 or 3/4 of the Mott-Dirac or Mott-Kagome bands, enabling the realization of a superconducting state with characteristics of a non-Fermi liquid. Future research plans involve the investigation of quantum Hall effects and unconventional superconductivity phenomena through the manipulation of adsorbed atoms, particularly focusing on spin-orbit coupling and magnetic property variations in the artificial lattice system.
다양한 위상 물질 중에서 위상 마디선 준금속은 위상적 특이점이 하나의 점이 아닌 길게 이어진 선(line) 형태로 존재하기 때문에 외부 전자기장에 대해 더 민감하 고 독특한 양자 효과가 있을 것으로 예측되었다. 그러나, 기존의 위상 마디선 준금속 후보물질은 위상학적으로 특이한 전자상태와 그렇지 못한 보통의 전자상태가 공존하고 있어 전도 특성에서 양자역학적인 효과가 관측된 사례가 매우 드물었다. 따라서, 위상 마디선 전자상태만 존재하는 물질의 합성과 그러한 물질에서 나타나는 독특한 양자 효과를 실험적으로 관측하는 것은 응집물질 물리 연구에 있어 중요한 과제이다. 연구진은 스트론튬-비소 화합물 (SrAs3)의 도핑농도를 정밀하 게 조절하며 위상학적으로 특이한 위상 마디선 전자상태만 유일하게 전도특성에 기여하는 단결정을 제작하였고, 이를 각분해 광전자 분광 실험 및 양자 진동 실험과 같은 다양한 실험을 통해 교차 검증하였다. 또한, 연구진은 해당 위상물질에서 위상 마디선 전자상태의 고유한 양자전도 효과인 2차원 약한 반국소화 현상이 나타나는 것을 관측하였다. 이러한 결과는 위상 마디선의 2차원적 성질로 인해 3차 원 물질에서도 2차원 양자간섭 현상이 나타나는 특이한 현상이다. 이러한 결과는 위상 마디선 전자상태의 고유한 양자전도 효과를 최초로 관측한 것으로, 향후 위 상 마디선 전자상태를 이용한 차세대 정보 소자 제작에 유용한 정보를 제공할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
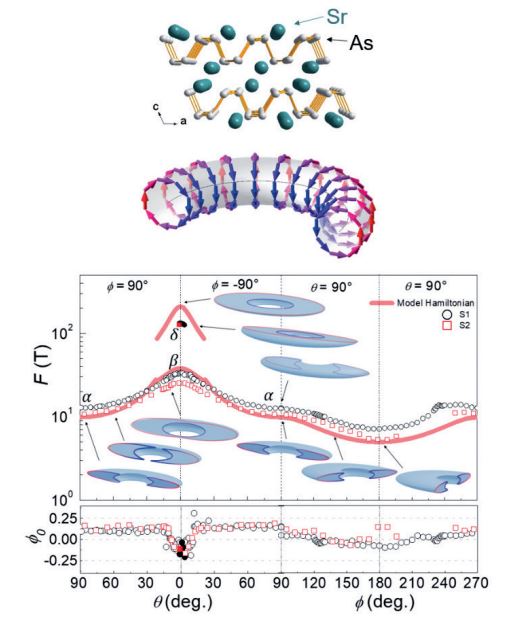
Figure. (Left top) Nodal-line semimetal candidate SrAs3 (Left bottom) Fermi surface and pseudospin texture of nodal-line electronic states (Right) Angle-dependent quantum oscillations and variation of Fermi surface crosssection and Berry phase.
Among the various topological materials, topological nodal-line semimetals were predicted to be more sensitive to external electromagnetic fields and exhibit unique quantum effects. However, previously investigated candidates for topological nodal-line semimetals not only host the nodal-line state but also topologically trivial states, which mask quantum mechanical effects in their conducting properties. The synthesis of candidate materials with only topological nodal-line states at the Fermi level and the experimental observation of their unique quantum effects are an important challenge in condensed matter physics. By precisely controlling the doping concentration of a strontium-arsenide compound (SrAs3), we produced single crystals in which the only topological nodal-line states contribute to conduction, which were confirmed by various experimental probes such as angleresolved photoelectron spectroscopy and quantum oscillations. We also observed a two-dimensional weak antilocalization phenomenon, a unique quantum interference effect of the topological nodal-line states. This unusual finding of two-dimensional quantum interference even in three-dimensional materials is the first demonstration of the unique quantum effect of topological nodal-line states and are expected to provide useful information for next-generation information devices using topological nodal-line states.
반데르발스 물질기반 스핀 접합 소자는 높은 결정성과 원자수준에서 깨끗하고 평평한 계면을 형성할 수 있어 스핀트로닉스 소자 응용성이 기대되어 최근 전세계적으로 활발히 연구되고 있다. 다양한 반데르발스 물질을 이용한 스핀 접합 소 자 연구를 통해 다양한 스핀트로닉스 기능성이 확인되었으나 기존 박막기반 스핀 트로닉스의 기능성을 월등히 개선한 결과는 제한적으로 보고되었다. 본 연구에서는 반데르발스 강자성체인 Fe3GeTe2와 반데르발스 부도체인 WS2 또는 hBN 를 이용한 접합 소자를 구성하고 기존 박막소자 대비 획기적으로 넓은 전압 인가 영역에 대해서 스핀 터널자기저항을 조사하였다. 접합에 인가되는 전압을 넓은 영 역으로 조절하여, 강자성체의 스핀 의존 상태 밀도의 급격한 변화를 유도하고 이를 통해 유효한 스핀 분극의 크기와 부호를 인가 전압을 통해 효과적으로 변조하였다. 이는 기존 금속박막 또는 반데르발스/금속 박막 기반의 소자에 비해 반데르 발스 기반 소자가 월등하게 높은 터널자기저항 변화폭을 가진다는 점을 의미할 뿐 만 아니라 인가전압에 따른 스핀 분극 조절이라는 새로운 개념을 제안한 성과이다. 이러한 결과는기존 박막기반 스핀 소자에서 불가능한 기능성을 확인한 드문 사례로, 향후 반데르발스 기반 스핀 정보 소자로의 활용 가능성을 높이는 데 기여 할 것으로 기대된다.

Figure (a) Sign changes of tunneling magnetoresistance as a function of applied bias voltages (b) Calculated spin-dependent density of states (c) Spin tunneling conduction at high applied bias. (d) Comparison of tunneling magnetoresistance with bias voltages for previously-studied magnetic tunnel junctions.
Spin junction devices based on van der Waals materials have been actively researched worldwide due to their high crystallinity and the ability to form clean and flat interfaces at the atomic level. These characteristics are expected to lead to novel applications in spintronics devices. Various spintronics functionalities have been confirmed through the studies of spin junction devices using different van der Waals materials. However, limited results have been reported that significantly improve functionality over those of conventional thin film-based spintronics. In this study, we constructed a junction device using Fe3GeTe2, a van der Waals ferromagnet, and WS2 or hBN, a van der Waals insulator. We investigated the tunnel magnetoresistance over a dramatically wider voltage application region than conventional thin-film devices. By controlling the voltage applied to the junction over a wide area, we induced a rapid change in the spin-dependent density of states, which effectively modulated the magnitude and sign of the spin polarization through the applied voltage. These results not only indicate that van der Waals-based devices have a significantly higher tunnel magnetoresistance variation than conventional metal thin film devices but also propose a new concept of voltage-dependent spin polarization control, which can be utilized in all van der Waals-based spin information devices in the future.
 Center for Artificial Low
Center for Artificial Low