Research Achievement
2018
위상준금속은 전도띠와 원자가띠가 점 또는 선으로 만나면서 위상학적인 특이점을 만드는 물질이다. 위상물질의 전자는 모멘텀 공간에서 위상학적 특이점 근처를 지날 때 독특한 양자효과로 인해 가상의 자기장하에 있는 것 같이 행동한다.
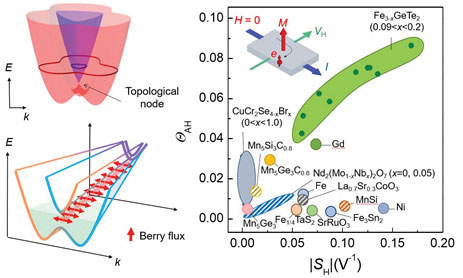
본 연구에서는 위상학적인 상태와 강자성 상태가 동시에 존재하는 강자성 위상준금속인 Fe3GeTe2에서 나타나는 강한 이상홀 효과가 이러한 위상전도 특성에 의해 나타난다는 것을 보였다.
Fe3GeTe2는 스핀 정렬 전자 상태가 모멘텀 공간에서 선으로 이뤄진 위상학적인 특이점을 갖는데, 이러한 위상특이점은 자기모멘트의 방향에 따라 그 성질이 달라지게 된다. 특히 Fe3GeTe2에서는 베리곡면 특성이 위상학적 특이점 근처에서 강하게 나타나게 되어 결과적으로 기존의 강자성체보다 강한 이상홀 효과가 나타난다. 이러한 Fe3GeTe2와 같은 위상 강자성체의 성질은 차세대 고감도 자성 센서나 스핀 정보소자 개발로 이어질 가능성이 있다. 또한 이번에 발견된 물질은 반데르발스 구조를 가지고 있어, 흑연에서 그래핀을 얻어내는 것처럼, 손 쉽게 2차원 강자성체로 변환이 될 수도 있다.
최근 전 세계적으로 활발히 연구되고 있는 2차원 반도체 물질 등과도 쉽게 결합 될 수 있는 장점이 있어 향후 2차원 물질에 기반을 둔 차세대 스핀소자 개발의 활성화도 기대된다.
Currently, topological semimetals, in which the conduction band and valence band are touching at some isolated points or lines in the momentum space, are one of the most interesting material classes, beyond topological insulators. Because of their peculiar band structure, the low energy excitations of topological semimetals can be described by relativistic Dirac or Weyl fermions, inducing topologically protected surface states and intriguing bulk properties.
So far, most of the studies on topological semimetals, especially those with nodal lines, are limited to nonmagnetic systems. One reason is that time-reversal symmetry plays a critical role for the degeneracy protection along the nodal lines in many topological nodal line semimetals. However, in the present work, we have found that if the system satisfies certain crystalline symmetries, a topological nodal line semimetal can be realized even in a ferromagnet with broken time-reversal symmetry, due to orbital-driven band degeneracy.
We propose a magnetic van der Waals (vdW) material Fe3GeTe2 as a candidate for the ferromagnetic nodal-line semimetal. Using first-principle calculations, angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy and magnetotransport property measurements, we show that the ferromagnetic nodal-line semimetal has various unusual physical properties, including the large anomalous Hall effect and the magnetically tunable nodal line degeneracy, which are not possible in the nonmagnetic systems.
Especially, the nodal line behaves likes a one-dimensional magnetic vortex line producing large Berry curvature, which is fundamentally a new mechanism generating large anomalous Hall current uncovered for the first time in the present work.
This work, therefore, demonstrates that Fe3GeTe2 is one of the most promising candidates for two-dimensional spintronic applications and will open a new avenue for investigating the intriguing interplay between topology and ferromagnetism in magnetic nodal-line semimetals.
궁극적 저차원 물질의 하나인 원자층 이차원 반도체는, 기존에 발현되지 않는 새로운 물질 특성과 더불어, 두께가 매우 얇고 면적이 매우 넓어 둘둘 말리는 전자기기, 사물인터넷 (IoT) 전자 부품, 극초소형 컴퓨터의 구현을 위한 차세대 반도체 후 보로서 전 세계적으로 주목 받고 있다. 이러한 연구 분야에서 기술적 난제는 고성 능의 회로를 만들기 위한 도핑 기술이 부재하다는 점이었다. 통상 상업적으로 사 용되는 기체 상태의 이온을 주입하는 도핑 기술은 원자 두께의 이차원 반도체를 구 조적으로 깨뜨릴 수 있고, 또한 농도를 섬세하게 조절하기 어렵다.
본 연구에서는 가시광 영역의 (파장 532 nm) 레이저를 이차원 반도체 물질에 조사함으로써 물질 내에 국소적인 원자결함을 만들 수 있고, 형성된 원자 결함에 의해 반도체 물질이 p-형 도핑이 됨을 밝히고 STM 계측을 이용하여 원자 수준에서 규명하였다. 또한 이 도핑 정도가 빛의 조사 시간에 따라 정교하게 조절될 수 있으며 반도체의 전도성을 10만 배 이상의 변위로 효과적으로 조절할 수 있음을 보였다.
특히, 본 연구에서는 빛을 이용한 도핑 공정을 통해 다양한 이차원 반도체 회로를 제작하는 데도 성공했다. 빛을 이용한 p-형 도핑을 통해 ‘이차원 반도체 광전압 변환기’와 ‘이차원 양극성 접합 트랜지스터’를 성공적으로 구현함으로써 본 도핑 공정이 실제 응용소자를 제작하는 데에 활용될 수 있을 만큼 효율적임을 입증하였다. 본 연구 결과는 빛과 물질간의 상호 작용을 이용한 원자층 이차원 반도체 물질 의 새로운 도핑 공정을 구현하였으며, 이의 미시적 도핑기작에 대해 규명하여, 기초 원천 연구가 직접적으로 소자 응용연구로 확장되었다는 점에서 큰 의의가 있다.
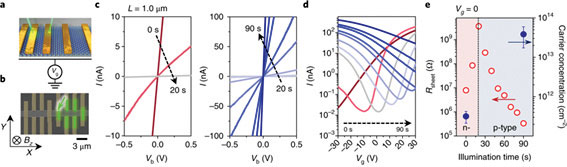
Figure 1. (a), Schematic of illumination-time-dependent p-doping on a 1-μm-long MoTe2 channelinaback-gated FET array. (b), SEM imageof Hallbardevices, where as canning laser illuminated the metal contacts marked by green dashedlines.
(c), I-V characteristics at laser illumination times from 0 to 90 s in increments of 10 s. (d), Corresponding transfer curves (I-Vg, at Vb = 50 mV, (e), Variationin the channel sheet resistances and carrier concentration swith illumination times from 0 to 90 s. Errorbars show the errorrange of carrier concentration in Hall measurement.
Atomic layer two-dimensional semiconductors, which are attracting attention as a next-generation semiconductor candidate globally, are a key material for the implementation of electronic devices, internet of things (IoT) components, ultra-compact computers. The technical challenge in the meantime was that there was no doping technology to make high performance electronic circuits.
Conventional doping techniques for injecting ions in liquid or gaseous state can break down thin two-dimensional semiconductors with atomic thickness, and it is difficult to finely control the concentration, which is a hindrance to commercialization.
In this study, we have found that localized atomic defects can be created in a semiconductor material by irradiating a laser (wavelength 532 nm) in the visible light to a two-dimensional semiconductor transistor element, and the semiconductor material becomes p-type doping due to the formed atomic defect. We verified such doping mechanism at the atomic scale with STM investigations.
In addition, the degree of doping can be precisely controlled according to the irradiation time of the light, and the conductivity of the semiconductor can be effectively controlled by 100,000 times or more.
In particular, this study succeeded in fabricating various 2D semiconductor circuits through the light doping process. The successful implementation of ‘two-dimensional semiconductor photovoltaic cell’ and ‘two-dimensional bipolar junction transistor’ through p-type doping using light proves that the present doping process is efficient enough to be used to fabricate practical application devices.
The results of this study show that it is possible to apply practical device on 2D material, which is attracting attention as a next-generation semiconductor material.
그래핀은 탄소 원자가 육각형 모양으로 모여있는 2차원 소재로서, 뛰어난 전기적 ∙ 광학적 특성 때문에 많은 관심을 받았다. 이러한 그래핀을 잘 쓰기 위해서는 무엇보다도 그래핀을 절연 기판 위에 대면적으로 준비하는 것이 필요한데, 이는 절연기판 위에 놓아야 전도성인 그래핀의 전기적 특성을 충분히 이용할 수 있기 때문이다. 이를 위해 많은 연구에서는 구리 포일 위에 그래핀을 대면적으로 성장한 후, 구리 포일을 제거하여 절연 기판으로 옮기는 전사 과정을 거쳤다. 하지만 이러한 전사 과정은 절차가 복잡하고 많은 화학물질을 사용하기 때문에 생성한 그래핀에 오염과 손상이 자주 발생하였다.
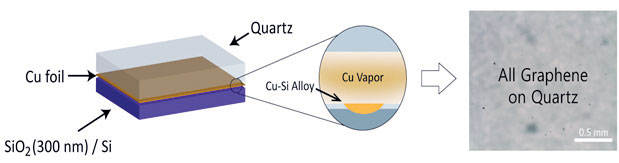
본 연구단은 저압화학기상증착법에서 구리 증기를 촉매로 사용하여 고품질, 대 면적, 단일층 그래핀을 절연 쿼츠 기판 위에 직접 합성하는 방법을 개발하는 데에 성공했다. 여기서 고농도의 구리 증기를 지속해서 생성하는 것이 대면적, 고품질 그래핀을 성장하는 데에 가장 중요한데 이를 실험적으로 구현하고자 구리 포일이 희생 기판으로 쓰이는 SiO2/Si 기판과 물리적으로 맞닿게 했으며, 그래핀 성장 기 판인 쿼츠 기판을 그 위에 포개어 놓았다. 이렇게 만들어진 샌드위치 구조를 고온 으로 가열하면 구리 포일에서 구리 일부가 실리콘 쪽으로 확산하면서 구리-실리 콘 합금을 형성하며, 이 합금이 구리 증기를 대량으로 생성한다. 이렇게 생성된 기 체는 샌드위치 구조 안에 갖혀 있게 되므로, 외부에서 들어오는 메테인을 효과적 으로 열분해하여 그래핀을 생성한다.
또한 전사과정없이 대면적으로 절연 기판 위에 직접 성장시킨 그래핀으로 이온성 액체를 사용한 차세대 반도체 소자를 제작하여 구현하였다.
Graphene is two-dimensional material composed of a hexagonal array of carbon atoms, and it shows outstanding electrical and optical properties. To fully take advantage of these fascinating properties, it is required to obtain high-quality specimen on an insulating substrate, because the insulation of the substrate guarantees full usage of the electrical properties of graphene itself. To accomplish this goal, previous researches have transferred graphene grown on Cu foil, but the transfer process was so complicated that the product was often damaged and contaminated.
Our group has successfully grown high-quality, large-scale, single-layer graphene on top of an insulating quartz substrate by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition using Cu vapor as a catalyst.
The key to the success is continuous supply of highly concentrated Cu vapor, which is achieved by the physical contact between a Cu foil and a sacrificial SiO2/Si substrate at high temperature; the high temperature makes evaporated Cu vapor diffuse into Si layer, yielding Cu-Si alloy that emits a large amount of Cu vapor.
Since this vapor is captured inside the specimen structure, it is possible to effectively decompose supplied methane to yield high-quality, large-scale graphene. We also fabricated high-performance semiconductor device using graphene on quartz without transfer, by using an electric double layer transistor with ionic liquid gating.
양자 컴퓨팅(quantum computing)의 기본 단위인 큐빗(qubit)은 연산 과정에 서 양자 결맞음 상태 (quantum coherence)가 유지되어야 한다. 자연계에 존재하는 안정적인 큐빗 상태는 정보처리 연구 분야의 새로운 패러다임이 될 것이며, 이는 광학물질계에서도 활발히 연구되고 있다.
본 연구진은 단원자층 ReS2에서의 엑시톤 준위를 광학적으로 여기시키면서 큐 빗 상태를 측정하는 데에 성공하였다. ReS2는 자연적인 비대칭 격자 구조체로 그 격자의 결에 의존적인 두가지 엑시톤 준위 X1, X2를 가지는데, 이 둘의 활성 편광축이 직각에 가깝기 때문에 선택적인 광여기와 결맞음 제어가 용이하다.
본 연구에서는 초고속 분광법을 이용하여 두 준위 사이의 양자 맥놀이 현상을 측 정하였고, 이를 통해 양자 결맞음 현상의 크기와 유효 시간을 계산해낼 수 있었다. 또한 각 엑시톤 준위가 레이저 편광에 의존적인 흡수를 한다는 것을 이용하여 선 형 편광의 각도만으로 양자 맥놀이의 경향을 제어하는 데에 성공하였다. 이 성과 는 저차원 반도체 시스템에서 구현한 큐빗 시스템의 몇 안 되는 사례 중 하나이며, 향후 다양한 양자 광학 분야로의 응용이 기대된다.
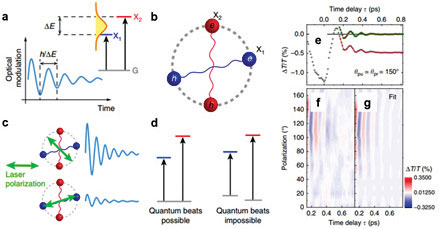
Figure 2. (a), Schematic of ultrafast quantum beat. (b), Schematic of exciton anisotropy. (c), Polarization-resolved control of excitonic quantum beats. (d), Condition for the ultrafast quantum beat. The ground state between two transitions must be shared. (e), Pump-probe transmission data for time delay. (f,g), Polarization-resolved differential transmission (f), and corresponding fit (g).
Quantum computing, a highly advanced form in existing computing process, requires the quantum coherence of the basic information unit. These basic units are called qubits, and research to find stable qubit states in nature is indispensable in the information processing industry where future paradigm shifts will take place.
Here, we have observed the quantum coherence triggered by optical excitation on exciton states of two-dimensional ReS2 layers. ReS2 is anisotropic layered materials, which involves anisotropic two exciton states X1, X2. Due to nearly perpendicular orientation for polarization of two exciton absorption, selective control of quantum coherence and optical excitation can be achieved. In this study, we employed ultrafast optical spectroscopy to measure quantum beat between two exciton states, and extract the effect lifetime of quantum coherence.
Furthermore, we have controlled the coupling of quantum coherence by rotating optcial polarization based on anisotropic absorption of exciton states. This achievement introduces the representative case of qubit design based on low-dimensional semiconductor system, and it is expected to pave the way on the wide range of research field in the quantum optics.
본 연구에서는 전자의 밸리 정보와 스핀 정보의 얽힘을 선택적으로 제어할 수 있는 이차원 이종 접합 소자 플랫폼을 최초로 구현하였다.
해당 소자는 전이금속 칼코게나이드 물질인 WSe2와 그래핀, 그리고 위상절연체 Bi2Se3가 순차적으로 접합된 구조 형태를 이루고 있다. 먼저 WSe2 층에 원형 편광된 빛을 쪼이면 특정 밸리의 전자가 선택적으로 여기되고 밸리-스핀 얽힘에 의해 특정 스핀 역시 선택적으로 여기된다. 이 정보는 WSe2에 연결된 전극에서 광전류의 형태로 검출된다. 한편 일부의 전류는 그래핀 채널을 통해 Bi2Se3 소자로 non-local diffusion의 형태로 전이되는데 밸리 정보가 배제된 스핀 정보만을 함유하고 있기 때문에 Bi2Se3 채널에서 광전류를 측정한다면 결합된 두 자유도 정보 중 스핀 정보만을 추출할 수 있다.
이러한 새로운 이종 접합 소자 구동을 통해 본 연구진은 기존의 밸리-스핀 얽힘 시스템이 해결해야만 했던 과제인 “자유도 얽힘의 제어”를 실현시켰으며, 고자기 장, 극저온 환경이 아님에도 불구하고 제어를 성공적으로 이루어냄으로써 보다 쉽 게 전자의 자유도를 제어할 수 있었다. 이러한 일련의 성과는 향후 저차원 물질 기 반의 소자 시스템을 집적회로 수준까지 발전시킨 연산소자 및 광전자소자로 응용 시키는 데에 중요한 지표가 될 것으로 기대된다.
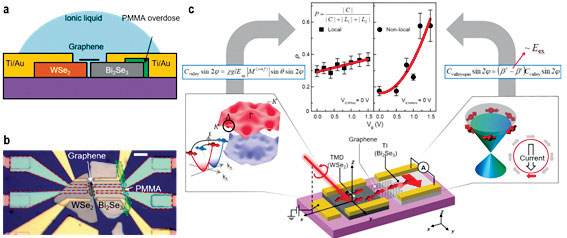
Figure 3. (a), Side-view of the WSe2-graphene-Bi2Se3 heterostructure device. (b), Optical microscope image of the heterostructure device. (c), Schematics for the generation, manipulation, and detection of valley-spin-coupled photocurrent. Polarization, P represents the fidelity of quantum degree-of-freedom, which has been modulated at the non-local measurement scheme.
We report the selectively controllable valley and spin degree-of-freedom in WSe2-graphene-Bi2Se3 heterostructure device. The device consist of the sequential connection of layered transition metal dichalcogenids WSe2, monolayer graphene, and three-dimensional topological insulator Bi2Se3.
The circularly-polarized optical excitation on WSe2 layer induce valley- spin-coupled quantum degree-of-freedom, which can be alternatively measured as valley polarized photocurrent in the WSe2 electrodes or diffused onto Bi2Se3 channel across graphene bridge. In latter case, non-local diffusion across the heterojunction only delivers spin polarization, thus Bi2Se3 channel can only measure the spin information. Based on this structure, we can extract the spin information from valley-spin-coupled states.
This study have been demonstrated the disentanglement of valley-spin-locked quantum information, which was challenging issues on the valleytronic optoelectronics.
Furthermore, our system does not requires extreme measurement condition, such as high magnetic field or cryogenic temperature, which provides convenient access of the manipulation.
스핀각도분해 광전자분광 장비는 포항 방사광 가속기의 4A2 빔라인에 설치되어 있으며, 휘도가 뛰어나고 편광 상태를 조절할 수 있는 넓은 에너지 영역의 photon 을 사용하기 때문에 실험실 장비보다 우수한 성능을 가질 뿐만 아니라, 저차원 물 질과 같이 비등방적 성질을 기본적으로 가지는 시료에 대한 다양한 실험적 접근 이 가능하도록 설계되었다. 2018년도에는 포항가속기와의 협약에 의해 50%의 가동시간을 외부 연구 그룹에 제공하였으며, 나머지 50%의 가동시간을 이용하여 연구단 내부연구, 실험환경 개선, 스핀검출기 개발 및 실시간 실험 셋업 개발을 수행하였다.
2018년 6월까지는 진공장치 개선작업, 제어장비 원격화, 모니터링 장치 통합 등을 통해 진동과 소음을 최소화하고, 스핀 검출기를 위한 장비를 설치할 수 있 는 공간을 확보하였다. 그 후에 스핀검출기를 설치하고, Fe 타겟 및 검출기 광학 계 최적화 작업을 시작하였으며 10월경에 (그림 4)에 보인 바와 같은 스핀 광전 자 분해 스펙트럼을 얻는데 성공하였다. 앞으로 계속된 개발을 통해 성능을 더 개 선할 예정이다.
이와 함께 연구단 내부 실험들의 성공적인 수행을 위해 실시간 실험 셋업 개발 을 시작하였다. 이 셋업은 광전자 분광기에 인접한 곳에 미세조절이 가능한 진공 증착기를 개발 설치하고, 진공증착을 하면서 각도분해 광전자 분광 스펙트럼을 얻 을 수 있도록 한 것인데, 첫 번째 실험결과를 (그림 5)에 나타내었다. 진공증착기 는 전자분석기를 오염시키지 않도록 최대한 같은 방향으로 설치하였으며, 전류 모 니터링 및 피드백을 통해 미세한 증착이 일정하게 유지되도록 하였다. 또한, 증착에 의해 전하가 도핑되는 속도에 맞추어 빔라인의 성능을 최적화하였다. 그림5의 (b)에 나오는 스펙트럼은 3분 안에 하나의 각도분해 분광 스펙트럼을 측정한 것인데 대단히 성공적으로 스펙트럼의 극적인 변화를 추적하는 데 성공하였다.
-
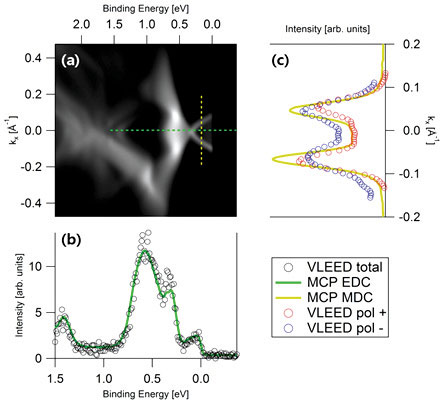
Figure 4. The first spin ARPES spectra taken for Bi2Se3 (a) ARPES image at the MCP plane. (b) The extracted spectrum from the image (green line) and the measured one with a channeltron at the Fe target stage (black circle) are compared. (c) Spin dependent spectra (blue and red circle) and a total spectrum extracted from the image (yellow line) are compared.
-
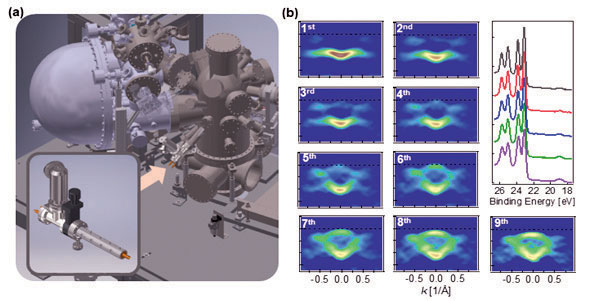
Figure 5. (a) The configuration of real-time measurement setup (b) Real-time drastic changes in the band structure are monitored with the setup. It takes three minutes to obtain each ARPES spectrum.
The CALDES end-station at 4A2 beamline port of Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL) is dedicated for spin-ARPES measurements on the low dimensional quantum materials. Highly brilliant photon beams allows to detect low energy excitation with high energy resolution and variously polarized beams from an elliptically polarized undulator empower the station a special capability to address the symmetry of a specific band structure as well.
In 2018, half of beamtimes were assigned to external users as the contract with PAL and the other half were used for the internal experiments and the new instrument development. Two highlights of 2018 are the first acquisition of spin dependent spectrum and real-time measurement setup for ARPES.
Two orthogonal VLEED (very low energy electron diffraction) type spin detectors are adopted for the 3D vector analysis of spin structure and they are connected to the image plane of DA30L electron analyzer through a single transfer lens system. This year, the electron transfer lens system was optimized with a channeltron placed at the Fe target plane and the growth and the alignment of Fe target were studied, and finally the first spin resolved spectra were obtained. As shown in Figure 4, the resolution is still worse than the total spectrum because of large inlet aperture size of the single transfer system. Next year, we will test an advanced version with additional electron lens.
Also, a real-time ARPES system was developed and the first experiment was demonstrated very successfully as shown in figure 5. The key ingredients of the system are a very sensitive evaporator for constant charge dosing and the high photon flux of the beamline for the fast ARPES measurement.
The evaporator is composed of a target heater stage and an ion beam current monitoring system. The beam current feedbacks the heater power and the atomic fluence is maintained constantly during the measurement. Also, very high beam flux of the beamline makes it possible to obtain an ARPES spectrum in every three minutes with fixed mode. In this experiment, more than 100 ARPES spectra are obtained while the dopant layer grows until 0.1 ML.
초고속 시분해 라만 분광기를 이용하면 일반적인 라만 분광기에서 관측되는 준 입자들의 시간에 따른 변화를 관측할 수 있다.
이는 강력한 펄스신호를 통해 의도적으로 물질계를 들뜬 상태로 만든 후에, 기 존의 기저상태로 복귀하는 찰나의 순간을 시간적으로 분해하여 준입자들을 관측하는 방법으로써 (i) 기저상태에 가까이 위치한 경쟁하는 물질상의 존재를 볼 수 있게 해주거나 (ii) 바닥상태에서 관측하기 힘든 준입자들의 동역학을 드러내 주거나, (iii) 혹은 다양한 준입자들을 시간척도로 구분해 낼 수 있도록 도와준다.
현재 실험을 위한 디텍터, 증폭기 등의 대부분의 장비가 이미 구비되어있는 상태이며 (그림 6), 마지막으로 중심파장의 변경이 가능한 펨토초 레이저가 2019 년 4월 중순에 설치 완료 될 예정이다.
Figure 6. Components of the Raman setup for time-resolved experiments.
Time-resolved Raman scattering allows one to measure time-evolution of quasiparticles observed in regular Raman scattering. A strong laser pulse is used to excite the system and the recovery to the ground state is followed as a function of time, which can reveal (i) competing phases with the ground state, (ii) informations of quasiparticle dynamics not readily accessible in the ground state, or (iii) differentiate among quasiparticles of different natures based on their time scales.
Most of the components used in this experiment such as detectors and amplifiers have already been secured (Figure 6), and the construction will be completed when the tunable-wavelength femtosecond laser is set up in April 2019.
본 연구단의 극저온 고자기장 주사터널 현미경 장비는, 2019년 3월에 최종 조립을 마치고 각종 상온 테스트를 수행중이다. 2018년 상반기에 주사 터널 현미경의 최종설계를 마치고, 현재 각종 부품을 구입하고 제작 중이다.
주사 터널 현미경 헤드가 냉동기 안에 부착될 때 필요한 각종 부품들과 냉동기 내부의 주사 터널 현미경을 위한 전선들을 배치하기 위해, 냉동기를 전체 분해하여 부품 및 전선 조립을 마치고 냉동기 전체 재조립하였다. 샘플 준비를 위한 초고진공 챔버는 냉동기 하단에 부착되었고, 터보 분자 펌프 2개가 진공을 담당하게 설치하고, 샘플 및 팁을 교환하기 위한 매니퓰레이터의 제작을 완료하여 설치하였다.(그림 7 참조).
냉동기 및 챔버의 초고진공 테스트 및 액체 헬륨을 이용한 밀리켈빈 냉동기 테스트를 2018년 9월에 완료하였다. (그림 8)에 보이듯이 주사 터널 현미경의 샘플 홀더 뒷면을 직접 눌러서 냉각하는 콜드 팁의 온도가 30 밀리켈빈 이하로 측정되어서 앞으로의 정상적인 운용이 예상된다. (그림 9)는 매니퓰레이터의 끝에 설치된 내시경으로 관측된 냉동기 부품 이미지를 보여준다.
-
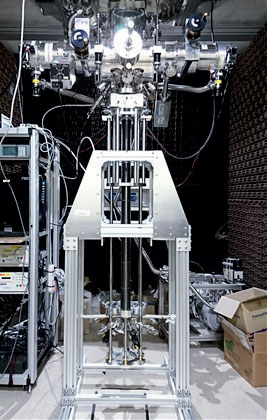
Figure 7. Vacuum Chamber and Manipulator
-
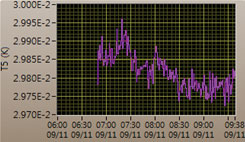
Figure 8. Cold Tip Temperature Graph
-
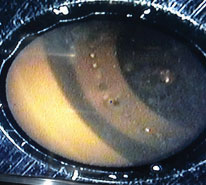
Figure 9. Endoscope Image
In March 2019, our center’s ultralow temperature high magnetic field scanning tunneling microscope has been assembled, and is under various testing at room temperature. Early 2018, the design of the scanning tunneling microscope has been finalized, and various parts and sub-assembly have been purchased or constructed.
To mount various electrical wires and many parts for the scanning tunneling microscope head receptacle in the ultrahigh vacuum space, the cryostat was diss embled. Many crucial parts were attached to the cryostat and the whole cryostat system was re-assembled. The ultrahigh vacuum chamber was mounted to the bottom of the cryostat, and two turbomolecular pumps was mounted to the sides to maintain the vacuum level of the system. Our manipulator, the most important component of the system, was assembled and mounted to the chamber (Fig. 7).
In September 2018, the vacuum and low temperature tests of the cryostat and the chamber has been successfully completed. As shown in Fig. 8, the temperature of the spring loaded col tip, which will be in thermal contact of the backside of the sample holder, was under 30 milli-Kelvin during the liquid helium testing. From this testing, successful operation is expected in the future. Fig. 9 shows the image through one of the endoscope mounted at the top of the manipulator.
주사 터널링 열전압 현미경은 탐침과 시료 간의 온도차이를 이용하여 저차원물 질의 열전기력을 원자수준의 높은 분해능으로 관찰할 수 있는 장비이다. 이는 상 온에서도 수 K정도의 온도차이로도 금속 표면의 standing wave pattern을 관 찰할 수 있는 높은 공간 분해능을 보여주며, 이를 활용하면 저처원 물질의 국소 결 함들이 저차원 물질 전자계에 미치는 영향을 살펴볼 수 있다.
특히 Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) 물질의 경우 이종접합구조, 원자수준의 결함 등에 대한 구조적, 열적 연구가 원자 수준에서 가능하다.
2017년 STVthM 을 위한 preparation chamber를 제작하 였고, 진공 펌프와 샘플 처리를 위한 시설을 구축하였고, 2018년에 STVthM 시스템을 조립하였다.
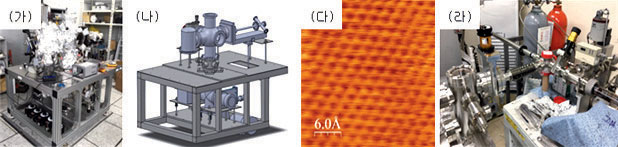
Figure 13. (가) Construction of STVthM (나) Schematic image of STVthM, (다) Atomically resolved topography of highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (라) Moving CVD sample under UHV condition
Scanning tunneling thermovoltage microscopy (STVthM) exploit a temperature gradient between the probing tip and sample to explore local thermoelectric power of the low dimensional electronic system.
STVthM presents an extreme spatial resolution down to the atomic level to investigate local thermoelectric properties of low dimensional materials. For example, few K difference at room temperature is sufficient to reveal surface standing wave patterns on single crystalline Cu(111) surface.
STVthM will play a crucial role in exploring a correlation between structural and thermal properties of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) and its heterostructure.
We started the construction of the new STVthM system in 2017 and prepared essential vacuum components and sample preparation system. The construction was proceeding and finished in 2018 with several upgrades, such as ultra-high vacuum (UHV) environments, heating stage, cleaving stage, MBE growth, and so on.
Moreover, we developed UHV-suitcase-compatible load-lock chamber, which allows the transportation of the as-grown sample from a chemical vapor deposition system into the STM/STVthM without breaking the vacuum condition.
공명 비탄성 X-선 산란은 방사광 가속기의 가변 에너지 빛을 이용하여 자성물 질에서 준입자의 에너지-운동량 관계를 관측하는 장비로 저차원 전자계의 새로운 물성을 밝히는 강력한 도구로 최근 주목받고 있다.
본 연구단에서는 국내 최초로 포항방사광가속기 1C 빔라인에 공명 비탄성 X-선 분광기 구축을 진행하고 있다. 분광기는 회절기가 도착하는 2019년 6월에 설치 가 본격적으로 시작될 계획이며 (그림 14), 2018년에는 이를 위한 사전 준비 작 업을 진행하였다.
1C 빔라인에서 제공하는 광원의 세기와 도넛형 집속 거울의 성능을 테스트하여 11 keV 에서 3x1011 photons/sec의 세기와 에너지 분해능과 직결되는 빔의 수직크기가 설계치(25μm)에 근접함을 확인하였다. 분광기의 설계 및 제작은 미국 Advanced Photon Source와의 기술협력을 통해서 이뤄지고 있다. 2020년에는 구축이 완료되어 표준 시료의 스펙트럼을 얻을 계획이며 1 eV 정도 범위의 스펙트럼을 50 meV 에너지분해능으로 2시간 내에 얻는 것을 목표로 하고 있다.
또한, 1C 빔라인에 이미 구축되어 있는 레이저 시스템을 이용하여 100 ps 수준 의 시분해 자기 회절 실험도 가능해서 2020년 이용자에게 개방되면 다양한 실험 환경을 제공할 수 있을 것이다.
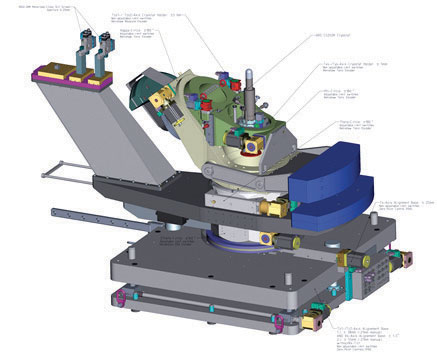
Figure 14. Kappa goniometer on which the RIXS spectrometer will be built.
Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) has recently emerged as a powerful tool to probe energy-momentum dispersion relations of elementary excitations in magnetic materials for understanding of the material properties of low-dimensional electronic systems.
Our center is establishing the first RIXS spectrometer in Korea at the 1C beamline of Pohang Light Source. The setup of the spectrometer will start in June 2019 when the goniometer arrives (Figure 14), and in 2018 we have performed preliminary tests of the beamline.
The x-ray at 11 keV provided by the 1C beamline was measured to have the intensity of 3x1011 photons/sec, and we have confirmed that the toroidal focusing mirror is capable of delivering the designed vertical beam width (25 μm) that is critical for the energy resolution. The design and manufacture of the spectrometer is carried out through a colloboration with Advanced Photon Source. We plan to take test spectra on reference samples in 2020 aiming for 50 meV resolutions with data acquisition time less than 2 hours for a ~1 eV range spectra.
Further, the 1C beamline is equipped with a laser system for timeresolved experiments with ~100 ps time resolution, which will provide a wide range of experiments for users when the beamline becomes open to users in 2020.
 Center for Artificial Low
Center for Artificial Low